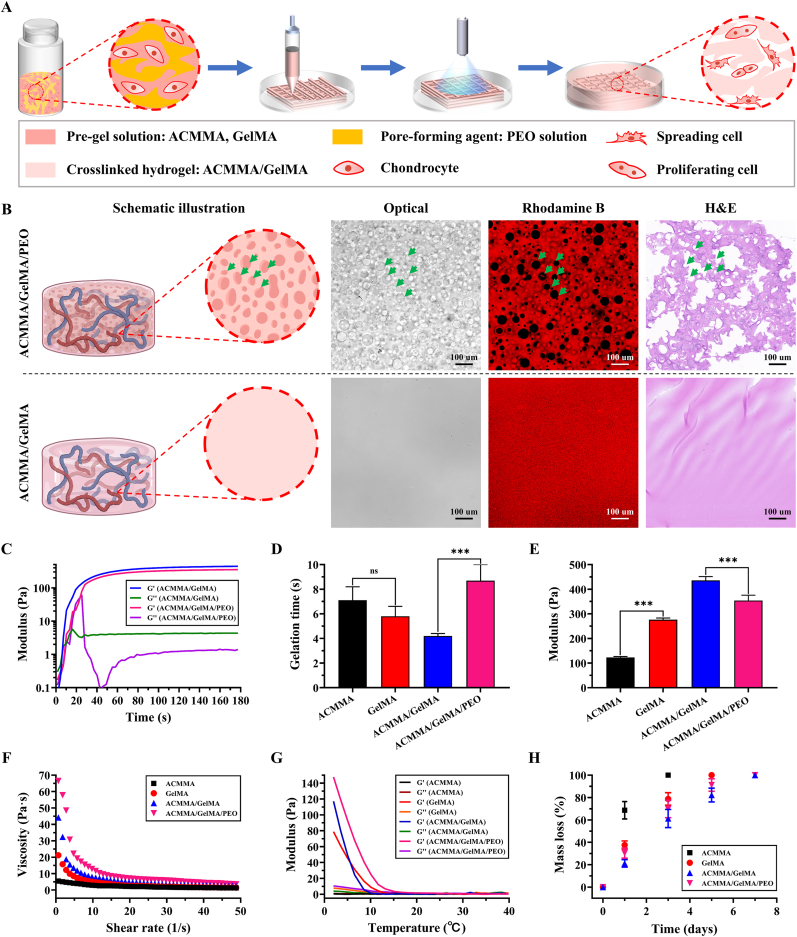
Fig. 3.
Physicochemical properties of microporous hydrogels. A) Schematics illustrating 3D bioprinted microporous hydrogels by dissolving PEO are beneficial to cellular behavior. B) The schematic illustration, as well as optical images, rhodamine B (the hydrogel networks conjugated with rhodamine B emitting red fluorescence, while dark areas indicate the micropores), and H&E showing the microporous structures compared with nonporous hydrogel. Rheological characteristics of bioink: C) Storage modulus (Gʹ) and loss modulus (Gʹʹ), D) Gelation time, E) Shear modulus, F) Viscosity performance, and G) Temperature-sensitive properties. H) Enzyme-mediated degradation of bioink. ns: p > 0.05. ***p < 0.001. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)