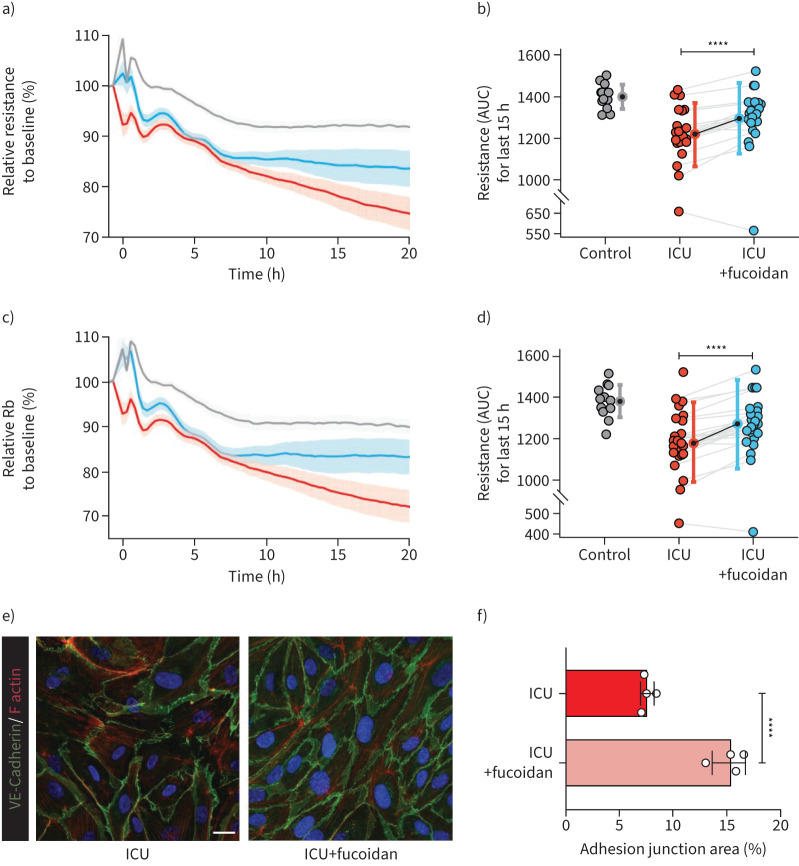
FIGURE 5.
Fucoidan could ameliorate endothelial cell barrier function in presence of serum of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) intensive care unit (ICU) patients. a) Barrier integrity parameter, resistance of primary human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (HPMECs) assessed by electric cell-substrate impedance sensing system (ECIS) in response to stimulation with 10% serum (at t=0 h) of healthy controls (n=12, grey line), COVID-19 ICU (n=26, red line) and COVID-19 ICU with fucoidan (n=26, blue line). Cell–cell contact parameter, Rb of c) HPMECs assessed by ECIS in response to stimulation with 10% serum (at t=0 h) of healthy controls (n=12, grey line), COVID-19 ICU (n=26, red line) and COVID-19 ICU with fucoidan (n=26, blue line). Data were normalised to the baseline resistance or Rb to calculate the relative resistance or Rb to baseline (%) and presented as mean±sem. b) Quantification of barrier integrity was based on the measurements of area under the curve (AUC) of final 15 h. d) Quantification of cell–cell contact was based on the measurements of AUC of final 15 h. e) Representative confocal images of VE-cadherin (green) and F-actin (red) staining on HPMECs in the presence of 10% pooled COVID-19 ICU serum with and without fucoidan (10 µg mL−1) for 24 h (scale bar=20 µm). f) Quantification of adhesion junction percentage of HPMECs in the presence of 10% pooled COVID-19 ICU serum with and without fucoidan (10 µg mL−1) for 24 h of four independent experiments. Graphs represent the mean±sd. Nonpaired and paired two-tailed t-test were performed. ****: p<0.0001.