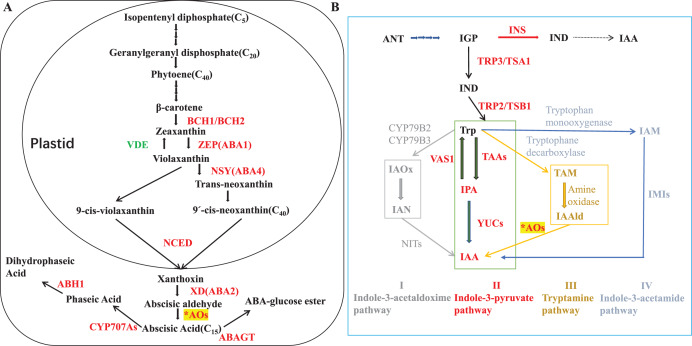
Figure 1. ABA and IAA biosynthesis.
(A) ABA precursor is synthesized from the methylerythritol phosphate (MEP) pathway. Enzymes are shown in red colour. BCH1/BCH2: β-carotene hydroxylases; ZEP: Zeaxanthin epoxidase; NSY: Neoxanthin synthase; NCED: 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase; XD: Xanthoxin dehydrogenase; ABAO: Abscisic aldehyde oxidase; CYP707A: ABA 8′-hydroxylase; ABH1: Phaseic acid reductase 1; ABAGT: ABA glucosyltransferase; βG: β-glucosidase; VDE: violaxanthin de-epoxidase, AOs: aldehyde oxidases were indicated with an asterisk (*). Adapted from Dejonghe, Okamoto & Cutler (2018); Song et al. (2020b); Finkelstein (2013). (B) ANT, anthranilate; IAA, indole-3-acetic acid; IAAld, indole-3-acetaldehyde; IAN, indole-3-acetonitrile; IGP, indole-3-glycerol phosphate; IND, indole; AAO, aldehydeoxidase; CYP79B2/3, cytochrome P450 monooxygenases2/3; IMI, amidase; INS, indole synthase; NIT, nitrilase; TAA, tryptophan aminotransferase; TRP3/TSA1, Trp synthase α-subunit; TRP2/TSB1, Trp synthase β-subunit; VAS1, pyridoxal phosphate-dependentaminotransferase1; YUC, YUCCA flavin-containing monooxygenase. Adapted from Kasahara (2016); Song et al. (2020a).