Table 5.
Current alternative therapeutical options for management of trypanocidal resistance.
| Trypanocidal agent | Trade names | Structure | Route of administration | Dosage (mgkg −1 ) b | Targeted trypanosome species | Adverse/side effects | Management of relapses |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diminazene aceturate | Berenil, Ganaseg Trypan Veriben Azidin Pirocide, |

|
IM | 3.5, 8 for resistant trypanosomes, 5-10 for T.b.evans. | T.congolense, T.vivax Less effective on T.b.brucei and T. evans | Has toxic effects in camels, horses, donkeys, and dogs, camels. | Isometamidium chloride |
| Isometamidium chloride | Veridium, Trypamidium, Securidium Samorin, |

|
IM | 0.25-1 | T. congolense, T. vivax less effective on T. b. brucei and T. b. evansi | Avoid subcutaneous administration. Highly painful, inflammation at site of injection in cattle, and highly cytotoxic at doses above 2mgkg_1. |
DA |
| Homidium bromide | Ethidium, Novidium |

|
IM, IV | 1 | T. vivax T.congolense. low efficacy on T. b. bucei infection in livestocks | Administation via IM cause toxic effcets to horses. It is highly carcinogenic |
DA and Isometamidium chloride |
| Quinapyramine sulphate | Antrycide, Triquin-S Trypacide, tribexin, Noroquin, and quintricide, |
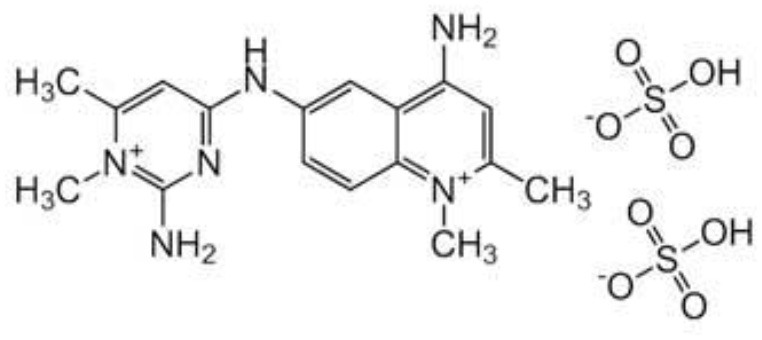
|
SC | 3-5 and 20-40 for T.simiae. |
T.b. evansi T.vivax T. congolense T. brucei T. b. equiperdum T. simiae/ camels |
Highly toxic at doses. High chances of resistances |
Isometamidium. Suramin sodium |
| Melarsomine dihydrochloride |

|
IM | 0·25-0.5 | T.b.evansi in camels | Has self-limiting side effects and immediate | Isometamidium. | |
| Melarsoprol | Mel B, Melarsen Oxide-BAL, Arsobal |

|
IV, given slowly | 2-3.6, given for three days After 1 week: 3.6 for 3 days Repeat again after 10-21 days: 3.6 mg/kg/day (69) |
Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense | Administered only in severe cases. Brain dysfunction, encephalopathy, convulsions, loss of consciousness, bloody stools, nausea, fever, vomiting, rashes, numbness, rashes, renal and liver disorders are all common adverse effects. It is not suggested for usage in pregnant women | eflornithine |
| Eflornithine | Vaniqas |
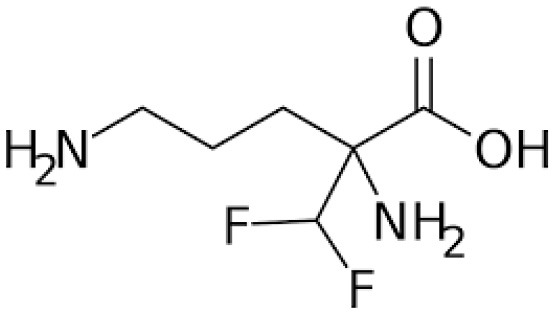
|
IV, administered slowly/ short tern infusions | 100, given at 6 h interval for 14 days - 150, in (children) |
T. b. gambiense | Bone marrow suppression resulting into anemia, leucopenia and thrombocytopenia, cancer, and alopecia, hypoacusis Best for patients above 12 years of age |
NECT |
|
Pentamidine (113) Other names: pentamidine diisethionate, pentamidine dimesilate |
For oral inhalation and for nebulizer use: •NebuPent Nebulizer (APP Pharmaceuticals LLC, United States) For IV and IM •United States and Canada: ° Pentacarinat 300 ° Pentam 300 ° Pentamidine isethionate 300 mg |

|
IV, IM, inhalation | 4 given IV/IM q d for 14–21 d | For early stage of T. b. gambiense | For the injectable formula: low blood sugar, irritation at the sit of injection, vomiting, nausea, low blood pressure, and kidney problems occur. For inhaled formula; patients experience nausea, wheezing, and cough, nausea Others may include; chest pain and skin rash |
Eflornithine or melarsoprol |
| Suramin sulphate | Naganol, Bayer 205, Germanin |

|
IV, Given as 3 doses per week in horses | A dose of 10mg Taken every 5 days to total of 12 injections for T. b. gambiense Adult: 100-200 mg (test dose) (IV), then 1 g IV on days 1, 3, 7, 14, 21 Pediatric: 20 mg/kg- 1 g/dose IV on days 1, 3, 7, 14, 21; not to exceed |
T.b. brucei, T.b. evansi, T.b. equiperdum | IM causes necrosis at the site. Cause toxicity in horses. Others include; Vomiting, Hives, Numbness and tingling, Nerve pain in extremities, Kidney damage, Blood disorders, pancytopenia, Shock, Optic atrophy |
Quinapyramine sulphate |
| Nifurtimox | Lampit by Bayer |

|
oral | recommended doses are 5 mg/kg per os three times/day for adults and 7 mg/kg three times/day for children for 14–21 days. 30 mg/kg/d for 30 d |
Trypanosoma brucei gambiense |
Diarrhea, convulsions, vomiting epilepticus and Reversible cerebellar syndrome (ataxia, nystagmus, tremors, and vertigo) was seen with high dose (30 mg/kg/day for 30 days). | NECT |
