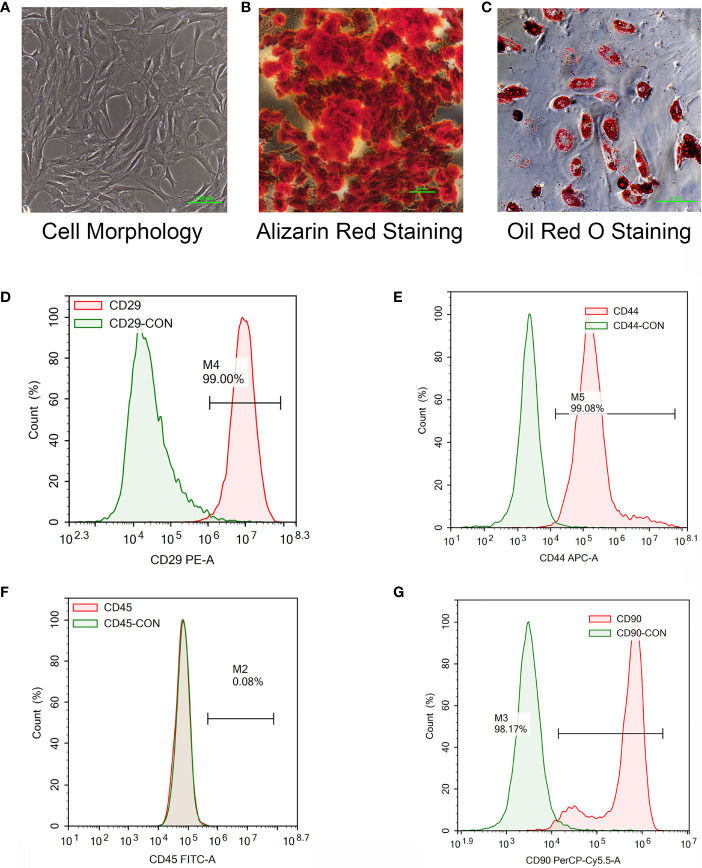
Figure 9.
Isolation and culture of rat primary BMSCs, the induction of osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation and the detection of cell surface markers. (A) The morphology of primary BMSCs from third-generation rats was observed under a microscope (×40). (B) After the osteogenic differentiation of third-generation BMSCs was induced with an osteogenic differentiation-inducing agent (Alizarin red staining), the formation of mineralized nodules was observed under a microscope (×100). (C) The adipogenic differentiation of third-generation BMSCs was induced by an adipogenic differentiation-inducing agent, and lipid droplets were enlarged and made rounder by continuous culture with maintenance medium (stained with oil red O) and observed under a microscope (×200). (D–F) The primary BMSCs of third-generation rats were collected and stained for CD29 (D), CD44 (E), CD45 (F) and CD90 (G) for 30 min. Control staining was simultaneously carried out. Fluorescence was detected with a flow cytometer, and the results were analysed.