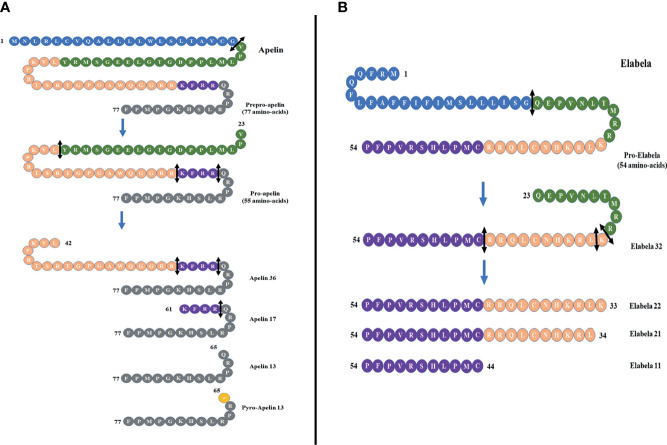
Figure 1.
(A) Different forms of apelin. The proteolysis of preproapelin at specific cleavage sites (double-headed arrows, black) leads to three fragments of 36, 17, and 13 amino acids named apelin-36, apelin-17, and apelin-13, respectively. The N-terminal glutamine residue of apelin-13 is pyroglutamylated, which produces the pyroglutamyl form of apelin-13 ([Pyr1]-apelin-13). (B) The proteolysis of proelabela at specific cleavage sites (double-headed arrows, black) leads to four fragments of 32, 22, 21, and 11 amino acids named elabela-32, elabela-22, elabela-21, and elabela-11, respectively.