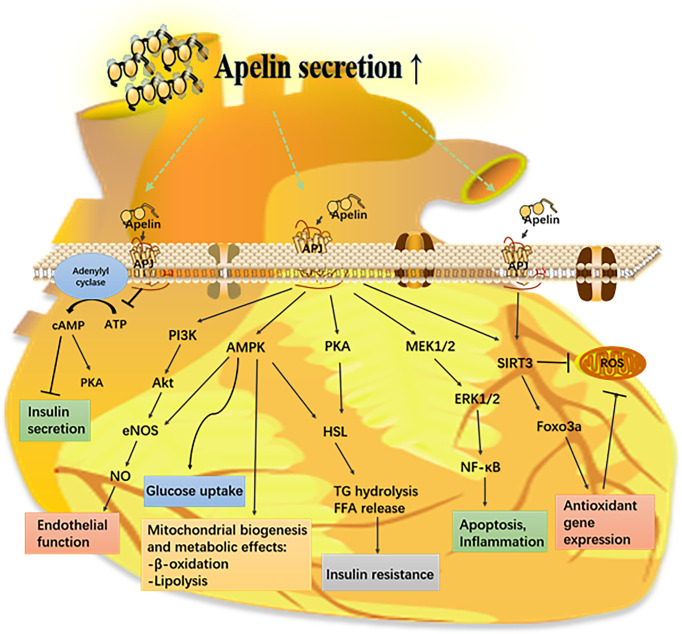
Figure 3.
Mechanism of the apelin–APJ system in diabetes and its complications. Apelin activates its receptor (APJ) and triggers various signaling pathways that have a protective effect on different organs from metabolic diseases. AMPK, AMP-mediated protein kinase; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; ERK1/2, extracellular-regulated kinases 1/2; FFA, free fatty acid; Foxo3a, forkhead box protein O 3a; HSL, hormone sensitive lipase; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PKC, protein kinase C; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SIRT3, sirtuin 3.