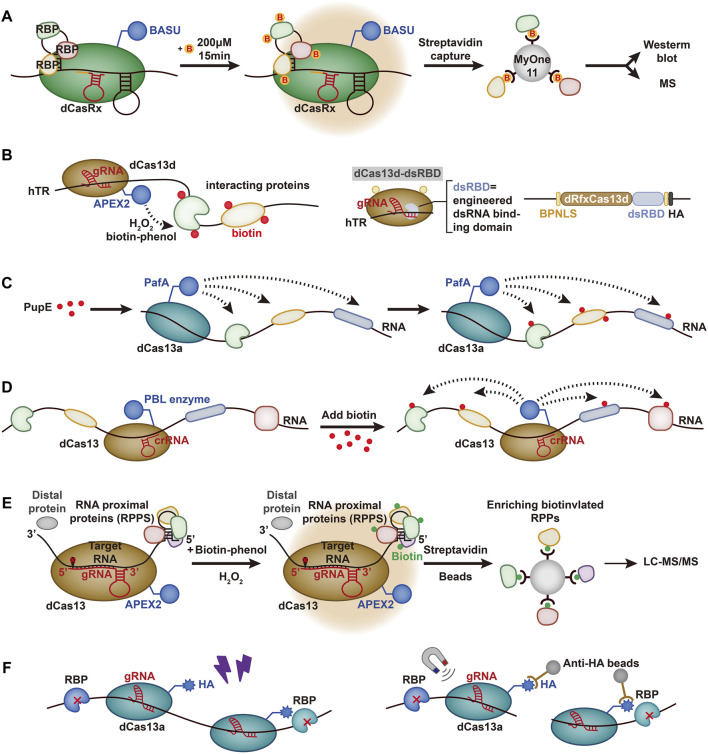
FIGURE 2.
Schematic representation of RNA-contented methods based on Cas13. (A) CARPID. dCasRx is fused with BASU. Biotin is represented by yellow circles marked with red “B.” CARPID is directed by dCasRx to target the RNA of interest, and the RBPs are biotinylated. (B) RNA–protein interaction mapping via Cas13-based APEX targeting. APEX2 is fused with dCas13d and targeted to the hTR with the help of gRNA. H2O2 is added to cells preloaded with biotin-phenol, which is oxidized by APEX2 to phenoxy and covalently labels proximal endogenous proteins. A sequence-independent double-stranded RNA binding domain (dsRBD) from human protein kinase R (PKR) is fused to the C-terminus of the dRfxCas13d protein to strengthen the stability and targeting ability. A bipartite nuclear localization sequence (BPNLS) is used to optimize nuclear localization. (C) CRUIS. PafA is fused with dCas13a to target the RNA of interest and modifies the surrounding proteins by mediating PupE. (D) CBRPP. PBL is fused with dCas13 and targets specific RNA to covalently tag the surrounding protein. (E) RPL. APEX2 is fused with dCas13 and biotinylates RNA proximal proteins with H2O2 and biotin-phenol mediated by gRNA. The biotinylated proteins are enriched by streptavidin beads and analyzed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). (F) CBRIP. dCas13a is fused with an HA tag and targets a specific RNA. RNA-protein interactions are stabilized by UV crosslinking, and the complexes are enriched by anti-HA beads.