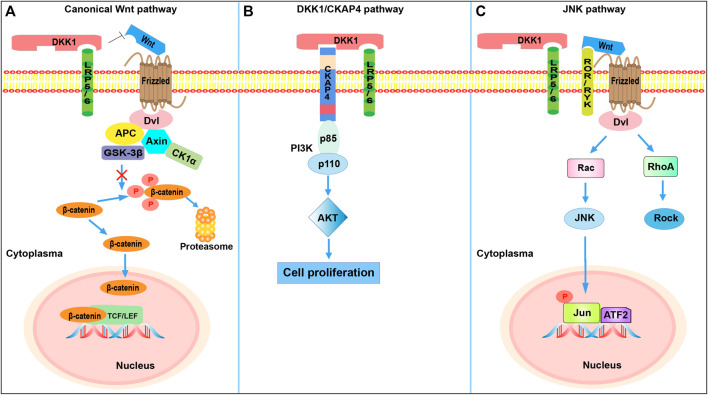
FIGURE 1.
The DKK1-involved signaling pathways. (A) DKK1-mediated inhibition of canonical Wnt signaling. DKK1 inhibits β-catenin-dependent Wnt signaling by binding to the LRP5/6 co-receptor and blocking Wnt binding, which results in β-catenin degradation. (B) DKK1-mediated activation of PI3K/Akt signaling. Binding of DKK1 to the CKAP4 receptor activates PI3K/Akt signaling and stimulates cell proliferation. When DKK1 binds to both LRP6 and CKAP4, cell proliferation is further promoted compared with binding of CKAP4 alone. (C) DKK1 activation of JNK pathway. The competitive binding of DKK1 to LRP5/6 shifts Fz receptors to the JNK pathway. Dvl, Dishevelled; Axin, axis inhibition protein; APC, adenomatous polyposis coli; GSK-3β, glycogen synthase kinase 3β; CK1α, casein kinase 1α; TCF, T-cell factor; LEF, lymphocyte-enhancer-binding factor; CKAP4, cytoskeleton associated protein 4; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase (consisted of p85 and p110 subunits); AKT, protein kinase B; ROR/RYK, receptor-like tyrosine kinase; Rac, Rac family Small GTPase; JNK, Jun N-terminal kinase; ATF2, activating transcription factor 2; RhoA, RAS homolog gene-family member A; Rock, Rho-associated coiled-coil-containing protein kinase.