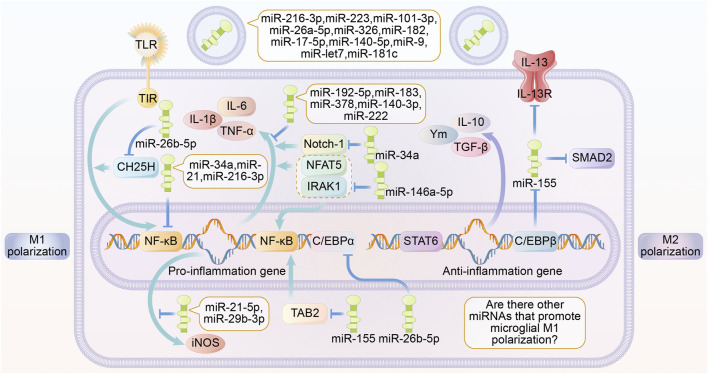
FIGURE 1.
Roles of exosome miRNA in microglia polarization. Different miRNAs secreted by exosomes are able to play a role in regulating microglia polarization through multiple signaling pathways. miR-216-3p, miR-223, miR-101-3p, miR-26a-5p, miR-326, miR-182, miR-17-5p, miR-140-5p, miR-9, miR-let7, miR-181c are able to inhibit TLR expression. miR-192-5p, miR-183, miR-378, miR-140-3p, miR -222 are able to directly inhibit the expression of inflammatory factors. miR-26b-5p inhibits the TLR signaling pathway by suppressing the expression of CH25H. miR-34a, miR-21, miR-216-3p are able to directly inhibit the expression of NF-κB. miR—21-5p, and miR-29b-3p inhibits the expression of the pro-inflammatory factor iNOS. miR-155 inhibits NF-κB activation by suppressing TAB2. miR-26b-5p inhibits C/EBPα expression. miR-146a-5p inhibits the expression of IRAK1 and NFAT5, thereby suppressing the expression of inflammation-associated genes and products. miR-34a inhibits the expression of Notch-κB. MiR-34a is able to inhibit Notch-1. The above miRNAs promote microglia M2 polarization and anti-inflammatory factor production. miR-155 promotes microglia M1 polarization and inflammatory factor production by inhibiting the expression of IL-13 receptor, SMAD2 and C/EBPβ. Abbreviations: TLR, toll like receptor; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; TGF β, transforming growth factor β; Ym, chitinase-like proteins; C/EBPα, CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein α; C/EBPβ, CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein β; TNF-α, tumour necrosis factor α; STAT6, signal transducer and activator of transcription 6; NF-κB, Nuclear factor kappa B; NFAT5, nuclear factor of activated T cells 5; IRAK1, interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase1; TAB2, TGF-Beta-Activated Kinase 1-Binding Protein 2; SMAD2, Sma- And Mad-Related Protein 2.