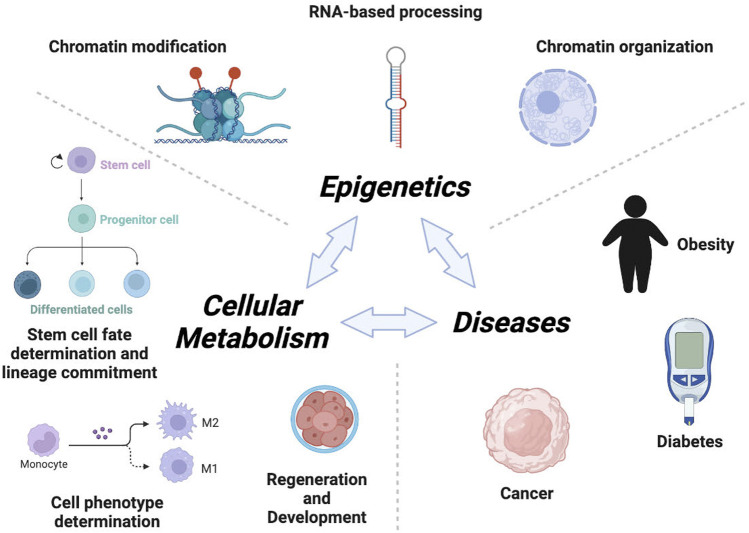
FIGURE 1.
Metabolism and Epigenetics co-ordinate the development and disease. Cellular metabolism, the basic physiological unit of an organism, is subject to epigenetic regulation. Key cellular decisions such as self-renewal, stem cell fate determination, lineage commitment, and functional specification are determined by epigenetic regulation. Metabolites fuel the epigenetic machine in the form of substrates or co-factors for chromatin remodeling enzymes. Impaired epigenetic regulatory mechanisms (chromatin modification, organization and RNA-based processing, etc) in cellular metabolism may shift the physiological equilibrium into an imbalanced state, potentially contributing to disease (e.g. obesity, cancer, diabetes, etc).