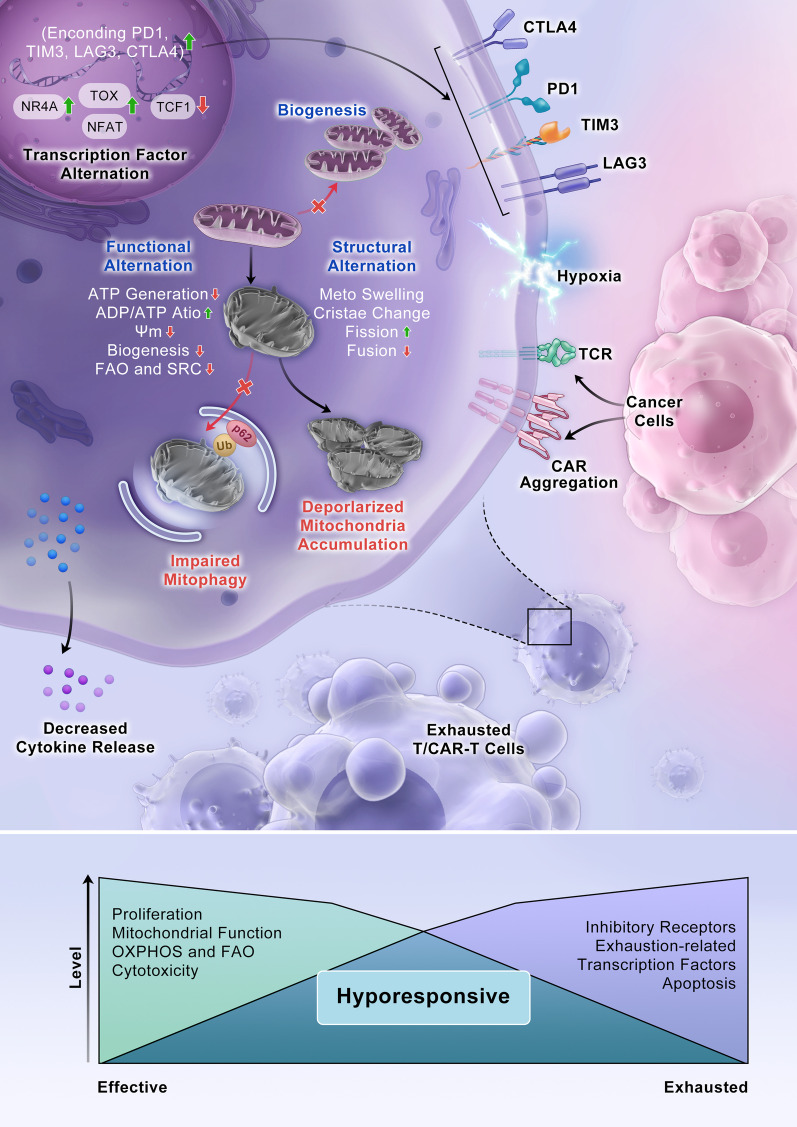
Fig. 1.
Features of T cell exhaustion and mitochondrial alterations. During persistent antigen stimulation and under hypoxia during chronic virus infection or cancer, CD8+ T cells enter a state of exhaustion. Tonic signaling in CAR-T cells is induced by autologous physical interactions between CAR receptors. Exhausted T cells and CAR-T cells exhibit decreased cytokine production and reduced proliferation capability; persistently high expression of multiple inhibitory receptors, such as PD-1, TIM-3, LAG-3 and CTLA4; and altered transcriptional landscapes, such as changes in changes in NR4A, TOX, TCF1 and NFAT transcription. Mitochondrial reprogramming characteristics in T cells include both functional and structural alterations. Mitochondria in exhausted cells are swollen and undergo increased fission. The mitochondrial cristae are slightly wider and more loosely organized in intermembrane regions. Functional alterations are characterized by an increased ADP/ATP ratio, decreased ATP generation and mitochondrial biogenesis, and decelerated fatty acid oxidation (FAO) and oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS)