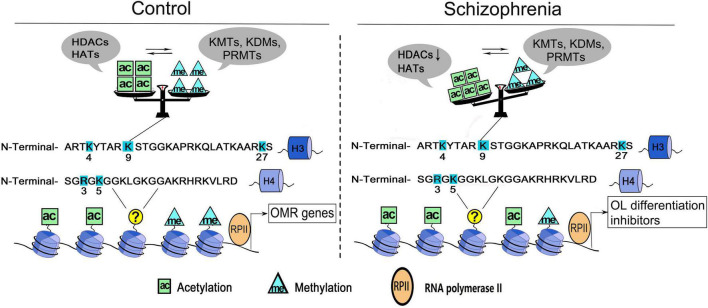
FIGURE 1.
A working model of histone acetylation and methylation underlying OLs dysfunction in schizophrenia. Histone acetylation and methylation at the promoters governing the expression of oligodendrocyte/myelin-related (OMR) genes. Multiple sites of H3 and H4 are dynamically regulated by histone acetyltransferases/deacetylases (e.g., HATs, HDACs) and/or histone methyltransferases/demethylases (e.g., KMTs, KDMs, and PRMTs). The cross-talk between two classes of enzymes secures the balance of epigenetic marks in OLs. In schizophrenia, the dysregulation of enzymes could change the balance/priority of histone acetylation and methylation at some key sites (e.g., H3K9), thus induce the reactivation of OL differentiation inhibitors and increase the cellular susceptibility. ac, histone acetylation; me, histone methylation; H3, histone 3; H4, histone 4.