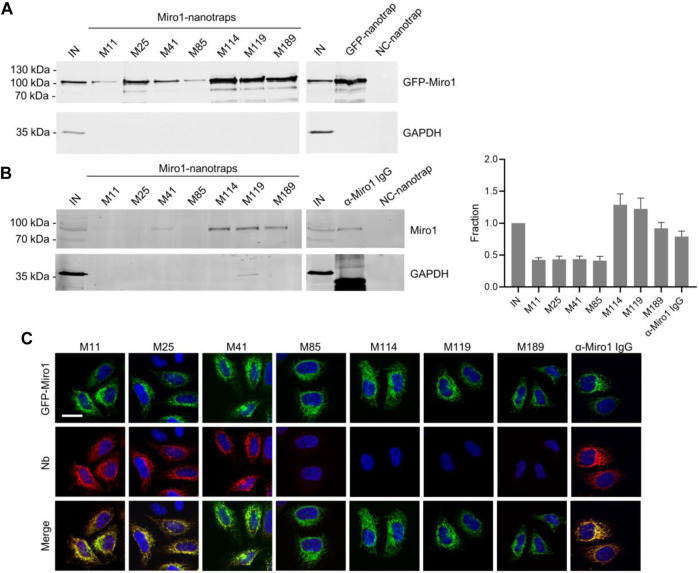
FIGURE 2.
Immunoprecipitation of Miro1 with Nbs. (A) For immunoprecipitation with immobilized Nbs (nanotraps), soluble protein fraction of HEK293 cells transiently expressing GFP-Miro1 or GFP as control, was adjusted to 2 mg/ml and incubated with equal amounts of nanotraps. Input (IN, 1% of total) and bound (20% of total) fractions were subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblot analysis using antibodies specific for GFP (upper panel) and GAPDH (lower panel). As positive control GFP-nanotrap and as negative a non-specific (NC) nanotrap were used. (B) Immunoprecipitation from non-transfected HEK293 as described in (A) were performed. Input and bound fractions were analysed with an anti-Miro1 antibody. As positive control anti-Miro1 IgG immobilized on Protein A/G sepharose and as negative control a non-specific (NC) nanotrap was used. For densitometric evaluation immunoblot signals of endogenous Miro1 in the corresponding bound fractions were normalized to the Miro1 signal in the input, which was set to 1. Shown are the mean signals from three independent biological replicates ±SD. (C) Immunofluorescence (IF) detection of GFP-Miro1 in fixed and permeabilized HeLa cells after staining with Miro1-Nbs as primary labelling probes. Representative confocal laser scanning (CLSM) images are shown of each individual Nb detected with anti-VHH antibody labelled with Cy5 (middle row). As positive control, transfected cells were stained with anti-Miro1 antibody followed by detection with a Cy5-labelled secondary antibody. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. Scale bar 20 µm.