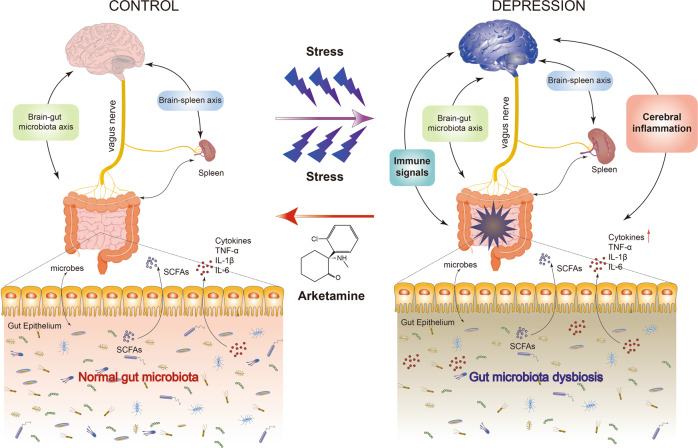
Fig. 3. Role of brain–gut–microbiota axis and brain–spleen axis in the stress-related psychiatric disorders and beneficial effects by arketamine.
Repeated stress caused gut microbiota dysbiosis and an increase in spleen size and weight, resulting in abnormalities in immune system. Stress-induced neuroinflammation might be mediated by the brain–gut–microbiota axis and the brain–spleen axis through the vagus nerve. Interestingly, arketamine could ameliorate the abnormalities of gut microbiota, abnormal functions of the spleen, and depressive symptoms in patients with stress-related disorders. A slight modification from the previous report [44]. Some materials of the figure have been designed using resources from Freepik.com.