Fig. 3.
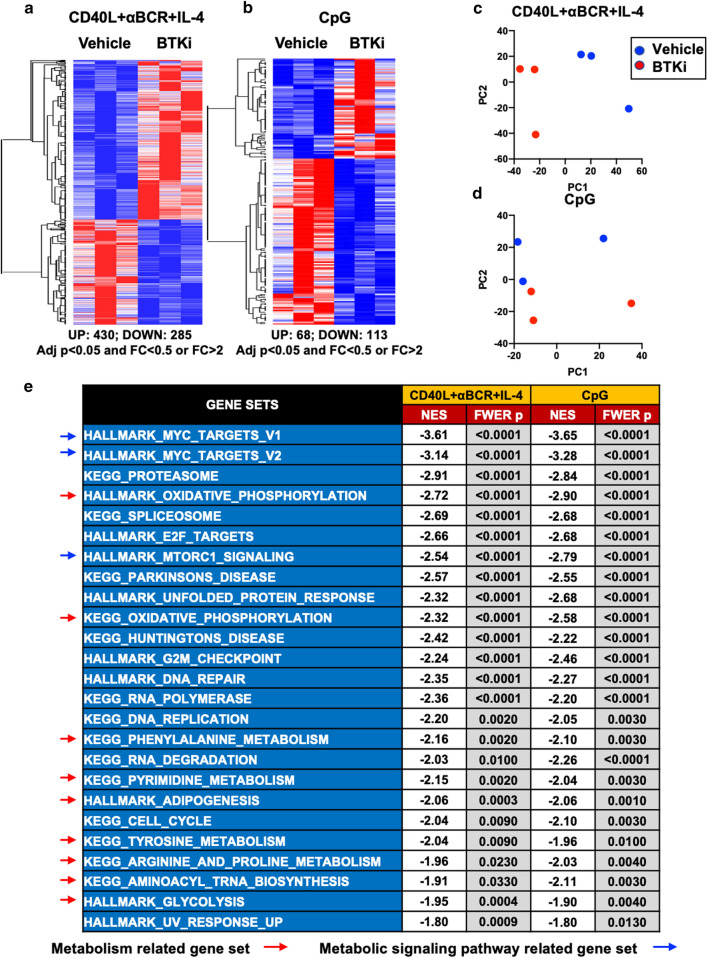
Transcriptomic changes induced by BTKi across different modes of B-cell activation. Purified healthy donor human B cells, pre-treated with either vehicle or BTKi for 30 min, were stimulated with either CD40L + αBCR + IL-4 or CpG for 18 h followed by bulk RNA-sequencing to test the impact of BTKi on activation-induced B-cell transcriptomic changes. Heatmaps together with hierarchical clustering (one minus spearman rank correlation) and principal component analyses were used to visualize the differentially expressed genes (a–d) with adjusted p value (Adj p) < 0.05; Fold change (FC) > 2 across different conditions (n = 3). Gene-set enrichment analysis (GSEA) against KEGG- and Hallmark-gene sets for those genes that were similarly impacted by BTKi across the stimulation conditions (e). As indicated by the negative NES (normalized enrichment score) values, 25 shared gene sets are inhibited in the BTKi condition relative to the vehicle control, among which nearly 50% (12/25) are implicated in either metabolic pathways (9/25, red arrows) or important signaling pathways that control metabolic processes (3/25, blue arrows)