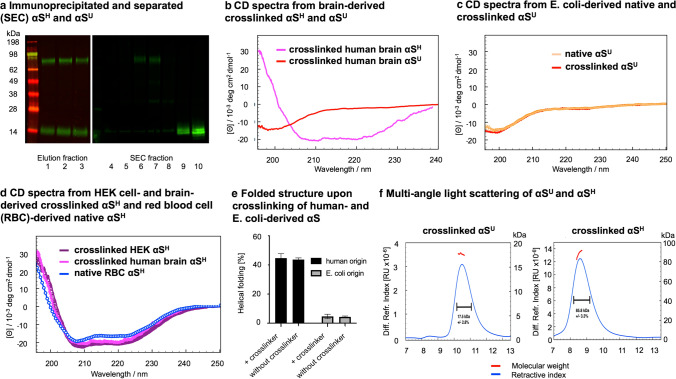
Fig. 1.
Cytosolic, multimeric brain-derived αS is helically folded and exhibits a mass of 86 kDa as demonstrated by circular dichroism spectroscopy (CDS) and multi-angle light scattering (MALS) analyses of purified αSH and αSU a Elution fractions 1–3 of a 2F12 anti-αS column incubated with a cross-linked control brain lysate showing the purification of the αS protein. On the right side, fractions 4–10 after size exclusion chromatography (SEC) are displayed showing the separation of αSH and αSU for downstream CDS and MALS analysis. b CDS of immunoprecipitated and separated (SEC) αSH and αSU from human frontal cortex control brain tissue upon cross-linking of brain lysate. The αSH from human brain exhibits an α-helical secondary structure of ~ 50%. c CDS of recombinant αS from E. coli. The recombinant αS is unfolded (~ 5% helical fold, ~ 95% unfolded, monomeric). The unfolded structure of recombinant αS from E. coli remains after cross-linking (~ 5% helical fold, ~ 95% unfolded, monomeric). d CDS of purified, native αSH from red blood cells (RBC) exhibits a secondary structure of ~ 45% helical fold and ~ 55% unfolded[4]. Cross-linked αSH from HEK cells exhibits an α-helical secondary structure of ~ 48% helical fold and 52% unfolded. The cross-linked αSH from human brain exhibits an α-helical secondary structure of ~ 50%. e Folded structure of αS without and with cross-linking demonstrating the difference from human and recombinant origin. f Immunoprecipitated αSU from frontal cortex tissue of a control was separated from αSH by SEC and analyzed via MALS demonstrating a mass of ~ 18 kDa. Immunoprecipitated αSH from frontal cortex tissue of a control was separated from αSU by SEC and analyzed via MALS demonstrating a mass of ~ 86 kDa