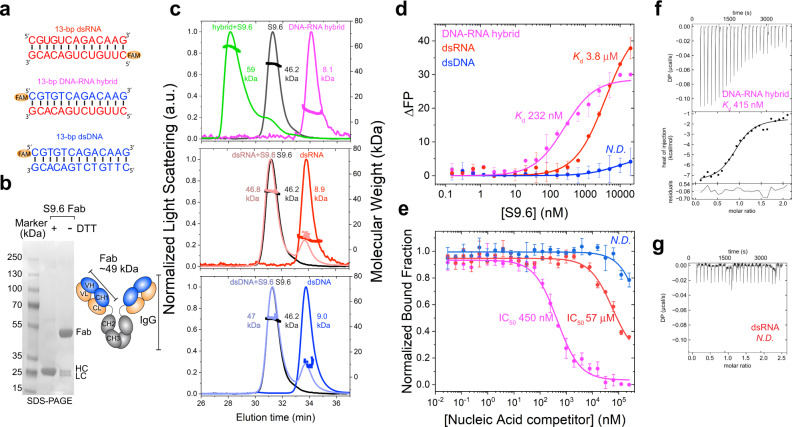
Fig. 1. Biophysical characterizations of nucleic acid binding preferences of S9.6 Fab.
a Sequences of double-stranded (ds) nucleic acids used for S9.6 characterizations and locations of FAM labels. b Schematic representation and denaturing SDS-PAGE analysis of S9.6 Fab in oxidizing and reducing conditions. SDS-PAGE analysis was performed twice. HC heavy chain, LC light chain. c SEC-MALS profiles of free S9.6 Fab (black), free DNA-RNA hybrid (magenta), free dsRNA (red), and free dsDNA (blue) and stoichiometric (1:1) mixtures of S9.6 Fab with hybrids (green), dsRNA (salmon), and dsDNA (light blue). SEC-MALS-derived molecular weights are indicated. d Binding affinity measurements of S9.6 Fab with nucleic acids in a by fluorescence polarization titration. Apparent binding constants (Kds) are indicated. Values are mean ± s.d. n = 3 biologically independent samples. ΔFP: changes in fluorescence polarization, in mP units. ND: not determined. e Competition experiments of fluorescently labeled DNA-RNA hybrids bound to S9.6 with increasing amounts of unlabeled nucleic acids, colored as in d. Apparent IC50s are indicated. Values are mean ± s.d. n = 3 biologically independent samples. f Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) profile of S9.6 binding to DNA-RNA hybrid. The measured binding constant is indicated. Values are mean ± s.d. n = 2 biologically independent samples. g ITC profile of S9.6 binding to dsRNA. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.