Figure 1.
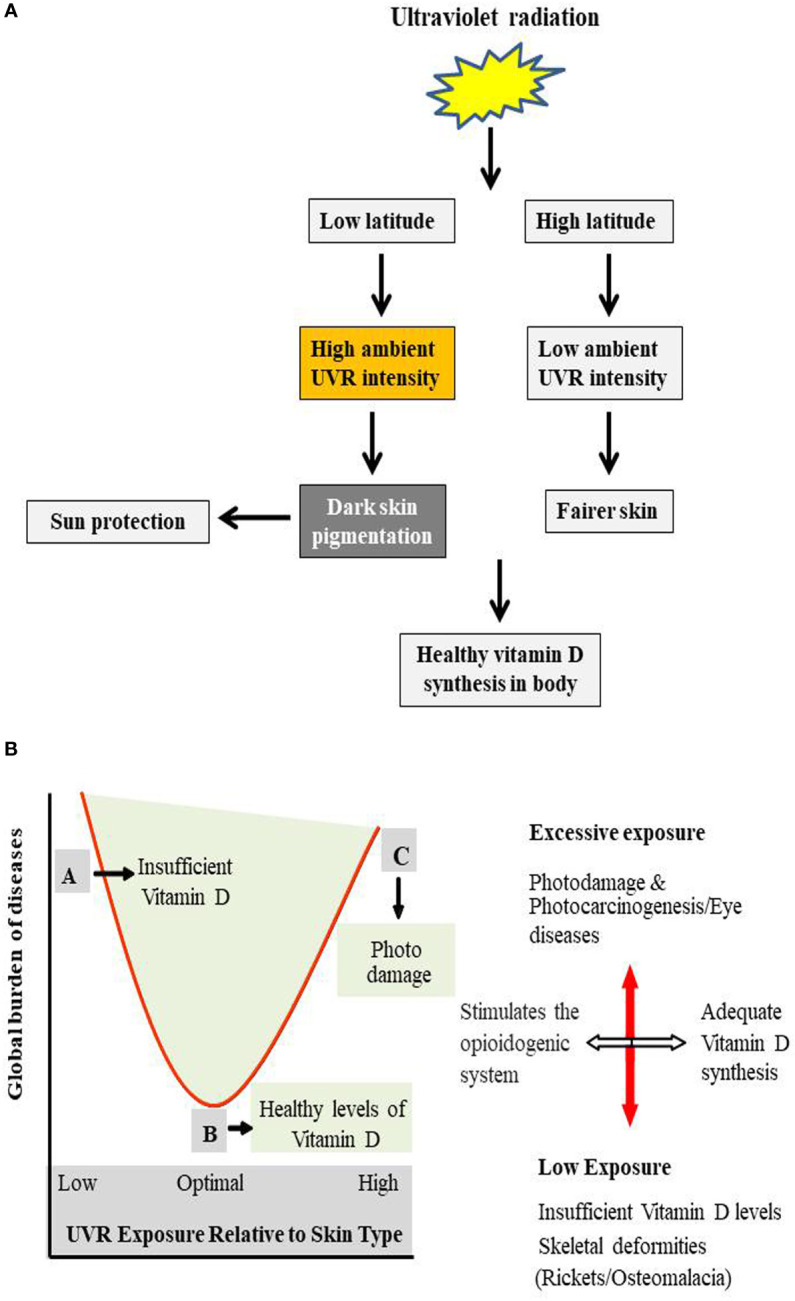
(A) Evolutionarily mediated adaptation of life forms to differential atmospheric UVR levels. UV radiation exposure requirements promoting healthy vitamin D synthesis in skin meant that people developed darker skin pigmentation at places of low latitude with high ambient UVR intensity, offering them protection from the effects of UVR. While, those at higher latitude have fairer skin as an evolutionarily developed trait to potentiate the insufficient vitamin D production from low ambient exposure of UV to skin. (B) Ambivalent effects of UVR exposure to skin. Schematic diagram showing relationship between benefits of optimum UVR exposure, ill effects of inadequate exposure and the global burden of diseases due to inappropriate UV exposure. A represents insufficient UVR exposure responsible for the improper vitamin D levels in the body leading to skeletal abnormalities and other indirect effects of low ambient UV exposure. B represents optimal UVR exposure required for the essential and healthy synthesis of vitamin D in the body and also stimulates the opioidogenic system in the brain. C shows high UVR exposure leading to skin and ocular malignancies especially, in fair-skinned individuals. Both A & C are related to inappropriate exposure of UVR to the skin.
