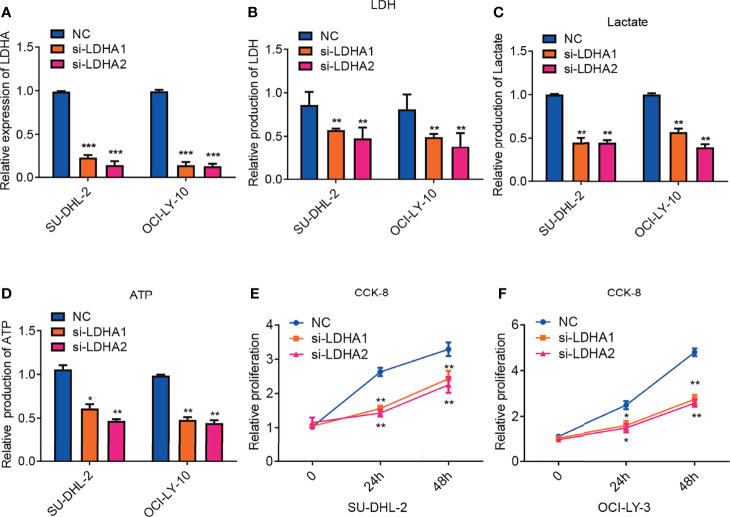
Figure 3.
Inhibition of LDHA attenuates glycolysis and suppresses tumor proliferation in ABC-DLBCL. (A) QRT-PCR analysis of LDHA mRNA expression in SU-DHL-2 and OCI-LY-10 cell lines. LDHA expression was detected after transfecting with siRNA of LDHA. Experiments were performed in triplicate, and data are presented as the mean ± SD. ***P < 0.001; one-way ANOVA. (B) downregulation of LDHA inhibits intracellular LDH in SU-DHL-2 and OCI-LY-10 cells. Experiments were performed in triplicate, and data are presented as the mean ± SD. **P < 0.01; and ***P < 0.001; one-way ANOVA. (C) inhibition of LDHA reduced intracellular lactate production in SU-DHL-2 and OCI-LY-10 cells. Experiments were performed in triplicate, and data are presented as the mean ± SD. **P < 0.01; one-way ANOVA. (D) inhibition of LDHA reduced ATP production in SU-DHL-2 and OCI-LY-10 cells. Experiments were performed in triplicate, and data are presented as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; and **P < 0.01; one-way ANOVA. (E, F) CCK8 proliferation assays were examined to determine cell proliferation of in SU-DHL-2 and OCI-LY-10 cells after transfecting with siRNA of LDHA. A multi-way classification analysis of variance tests was performed to assess data obtained from the CCK8 assays and data are shown as mean ± SD in the bar graph for three independent experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.