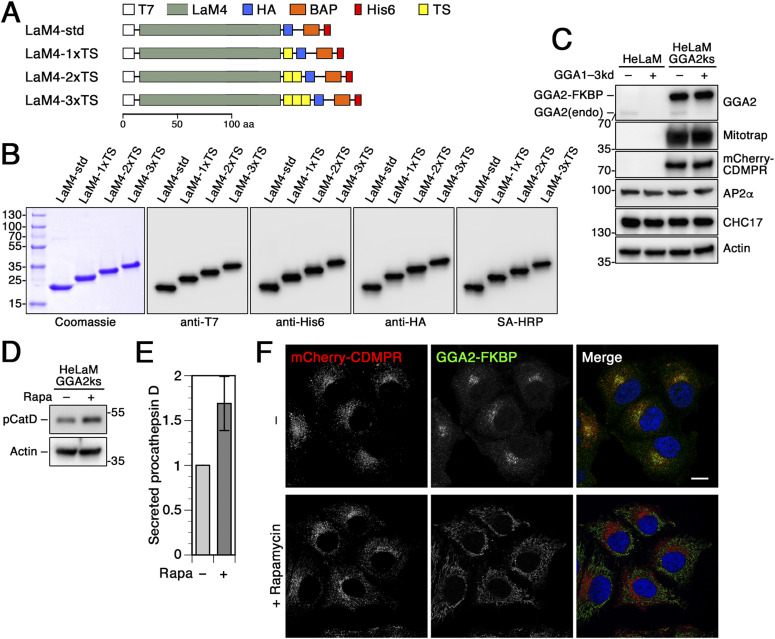
Figure 6. Derivatized anti-mCherry nanobodies for use with GGA2 knocksideways cells.
(A) Schematic representation of the functionalized anti-mCherry nanobodies. The standard nanobody (LaM4-std) consists of the mCherry-specific LaM4 domain, T7 and HA epitope tags, a biotin acceptor peptide (BAP), and a hexahistidine (His6) purification tag. Other nanobodies in addition contain one to three tyrosine sulfation sequences (TS). Scale bar in aa. (B) Bacterially expressed and purified nanobodies (30 μg) were analyzed by SDS-gel electrophoresis and Coomassie staining (left). Immunoblot analysis of nanobodies (10 ng) with antibodies against the HA, His6, or T7, or with streptavidin-HRP (SA-HRP). Marker proteins with molecular weights in kilodalton are shown on the left. (C) Parental HeLaM cells and HeLaM-GGA2ks cells stably expressing mCherry-CDMPR were transfected with non-targeting siRNA (−) or siRNAs silencing endogenous GGA1–3 (+). Cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis with antibodies against the indicated proteins. (D) HeLaM-GGA2ks cells stably expressing mCherry-CDMPR were transfected with siRNAs targeting endogenous GGA1–3. These cells were transfected with a plasmid expressing His6/myc-tagged procathepsin D 24–36 h before analysis. Media of cells incubated for 2 h in serum-free medium supplemented with 5 mM mannose-6-phosphate to prevent cathepsin D binding to surface MPRs, and with or without rapamycin (+ or − Rapa, respectively) were analyzed by collecting procathepsin D (pCatD) with Ni/NTA beads and immunoblotting with anti-myc antibodies. Cell lysates were immunoblotted for actin as a control. (E) Procathepsin D missorted upon knocksideways of GGA2 (+Rapa) was quantified from immunoblots as shown in panel (D), normalized to the DMSO-treated (−Rapa) control (mean and SD of four independent experiments). (F) HeLa-GGA2ks cells stably expressing mCherry-CDMPR after silencing endogenous GGA1–3 were treated with or without 500 nM rapamycin for 1 h and processed for fluorescence microscopy to detect mCherry-CDMPR and recombinant GGA2-FKBP. Bar: 10 μm.