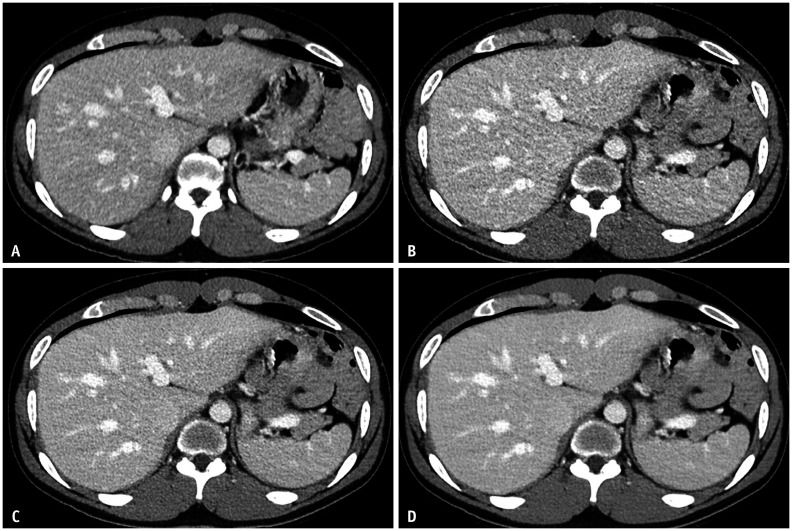
Fig. 2. Follow-up SDCT and LDCT protocol contrast-enhanced abdominopelvic CT images of a 61-year-old male with colon cancer; SDCT and LDCT studies were performed within one year of each other.
A-D. Axial CT images were taken at the same anatomic level to compare image quality between the SDCT protocol (A) and LDCT protocol (B-D). SDCT images were reconstructed with h-IR (A), while LDCT images were reconstructed with h-IR (B), DLIR-M (C), and DLIR-H (D). Image noise in the liver in CT images A, B, C, and D is 10.8, 16.1, 12.8, and 8.4, respectively. Quantitative measures of image noise, signal-to-noise ratio and contrast-to-noise ratio, show equivalence between SDCT with h-IR images (A) and LDCT with DLIR-M images (C). DLIR-H = deep learning image reconstruction high-strength, DLIR-M = deep learning image reconstruction medium-strength, h-IR = hybrid iterative reconstruction, LDCT = lower-dose CT, SDCT = standard-dose CT