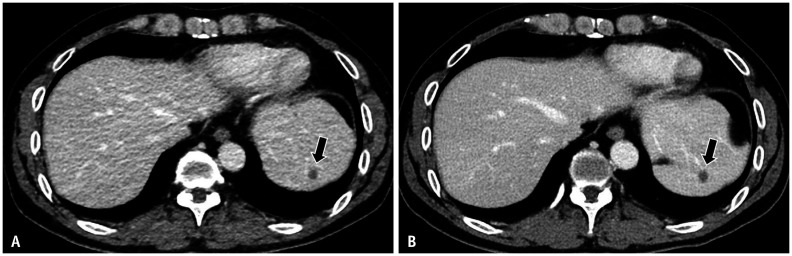
Fig. 3. A side-to-side comparison of qualitative measures between SDCT with h-IR images (A) and LDCT with DLIR-M images (B) of a 55-year-old male with colon cancer.
A, B. Black arrows show a focal liver lesion being assessed for lesion conspicuity. In terms of overall image quality and lesion conspicuity, all readers interpreted the LDCT with DLIR-M images (B) as being marginally superior (all score 4) to the SDCT with h-IR images (A). Although the image texture of SDCT with h-IR images was preferred over that of LDCT with DLIR-M images, the qualitative parameters of LDCT with DLIR-M images including overall image quality, image noise, image sharpness, and lesion conspicuity were comparable or superior to those of SDCT with h-IR images. DLIR-M = deep learning image reconstruction medium-strength, h-IR = hybrid iterative reconstruction, LDCT = lower-dose CT, SDCT = standard-dose CT