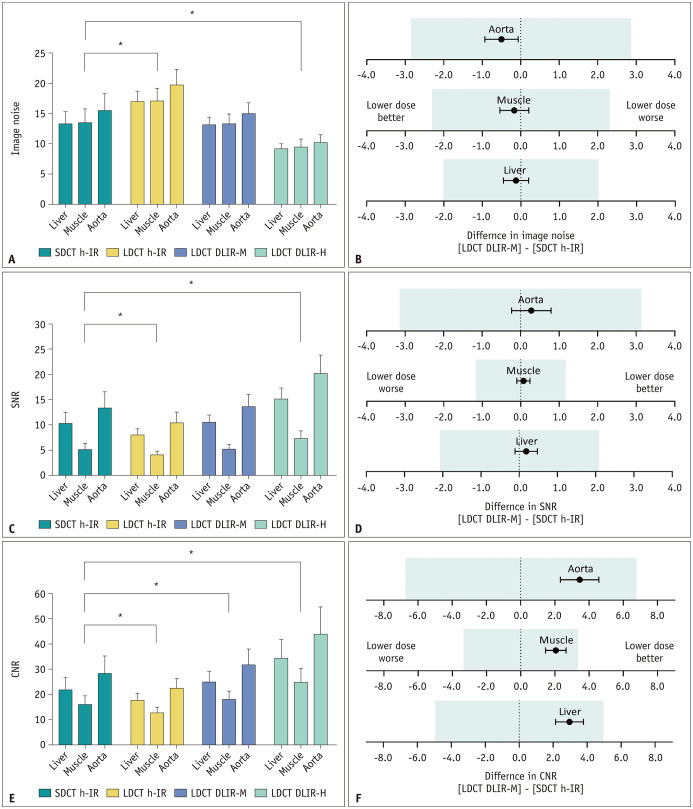
Fig. 4. Results of the quantitative image analysis.
*Statistically significant difference (p < 0.001).
A, C. The bar graphs show no significant difference between SDCT with h-IR images and LDCT with DLIR-M images in terms of image noise (A) and SNR (C). B, D, F. Equivalence tests show that LDCT with DLIR-M images are equivalent to SDCT with h-IR images with their prespecified margins (colored boxes in each figure part) in terms of image noise (B), SNR (D), and CNR (F). E. Regarding CNR, all LDCT images are significantly different from SDCT with h-IR images regardless of reconstruction method, but the difference between the mean values in LDCT with DLIR-M images and SDCT with h-IR images is the smallest. CNR = contrast-to-noise ratio, DLIR-H = deep learning image reconstruction high-strength, DLIR-M = deep learning image reconstruction medium-strength, h-IR = hybrid iterative reconstruction, LDCT = lower-dose CT, SDCT = standard-dose CT, SNR = signal-to-noise ratio