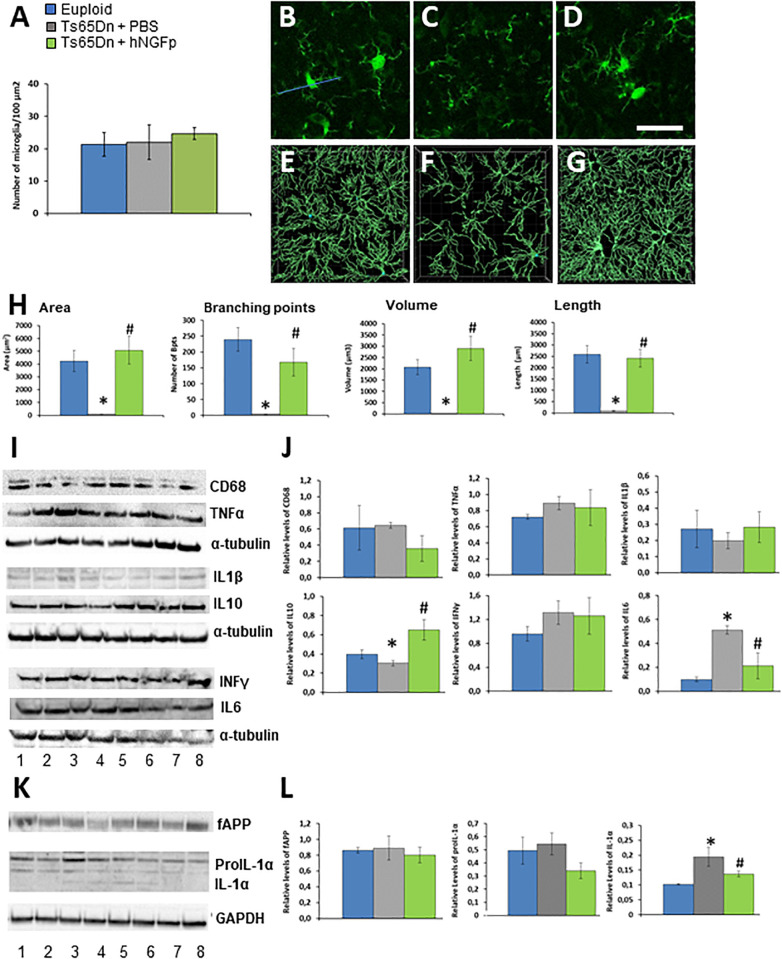
FIGURE 1.
Intranasal hNGFp ameliorates microglial dystrophic morphology and reduces IL-1α levels in Ts65Dn mice. (A) Density of microglia cells in euploid, Ts65Dn mice treated with PBS or hNGFp. Immunohistochemistry for IBA-1 in cerebral cortex revealed morphological changes in panel (C) Ts65DN microglia with respect to panel (B) euploid mice. (D) hNGFp treatment rescues these morphological changes. Reconstruction of microglia cells by IMARIS: (E) euploid (F) Ts65Dn (G) NGFp-treated Ts65Dn mice. (H) Quantification of microglial morphological parameters. Bars are representative of mean ± SEM. *P < 0.001 vs. euploid mice, #P < 0.001 vs. Ts65Dn mice. N = 6/group. (I) Representative western blots and (J) densitometric analysis for CD68, TNFα, IL-1β, IL-10, and IL-6. (K) Representative western blots for APP and IL-1α species. Lanes 1–2 = euploid mice; 3–5 = Ts65Dn mice treated with PBS; 6–8 = Ts65Dn mice treated with hNGFp. (L) Densitometric analysis of APP, proIL-1α (graph on the left) and mature IL-1α (right panel) levels. Values have been normalized to GAPDH values. Bars are representative of mean ± SEM. *P < 0.001 vs. euploid mice, #P < 0.001 vs. Ts65Dn mice. N = 6/group. Scale bar = 10 μm.