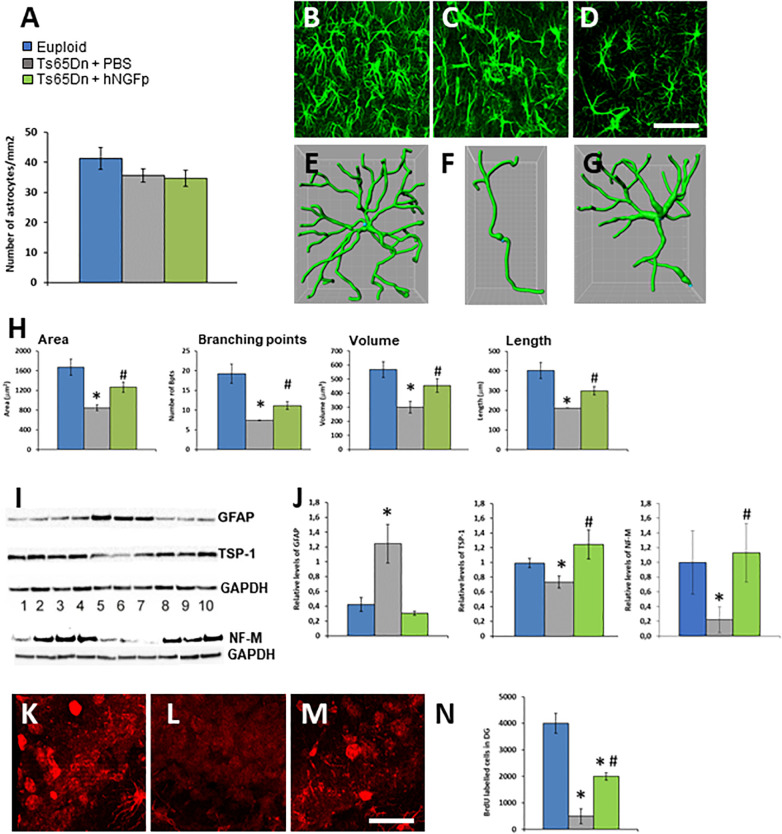
FIGURE 2.
Intranasal hNGFp rescues astrogliopathy and neurogenesis deficit in Ts65DN mice. (A) Density of astrocytes in euploid, Ts65Dn mice treated with PBS or hNGFp. Immunohistochemistry for GFAP in hippocampus revealed morphological changes in panel (C) Ts65DN astrocytes with respect to panel (B) euploid mice. (D) hNGFp treatment rescues these morphological changes. Reconstruction of astrocytes by IMARIS: (E) euploid (F) Ts65Dn (G) NGFp-treated Ts65Dn mice. (H) Quantification of astrocytic morphological parameters. Bars are representative of mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 vs. euploid mice, #P < 0.05 vs. Ts65Dn mice. N = 6/group. Scale bar = 35 μm. (I) Western blot for GFAP, TPS-1 and NF-M. Lanes 1–4 = euploid mice; 5–7 = Ts65Dn mice treated with PBS; 8–10 = Ts65Dn mice treated with hNGFp. (J) Densitometric analysis of GFAP, TPS-1, and NF-M levels. Values have been normalized to GAPDH values. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis is deficient in Ts65Dn mice compared to littermates and it is partially rescued by treatment with hNGFp. (K–M) examples from panel (K) euploid, (L) Ts65Dn, and (M) Ts65Dn dentate gyrus. (N) Stereological quantification of BrdU-labeled cells. Bars are representative of mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 vs. euploid mice, #P < 0.05 vs. Ts65Dn mice. Scale bar = 200 μm.