Figure 52.
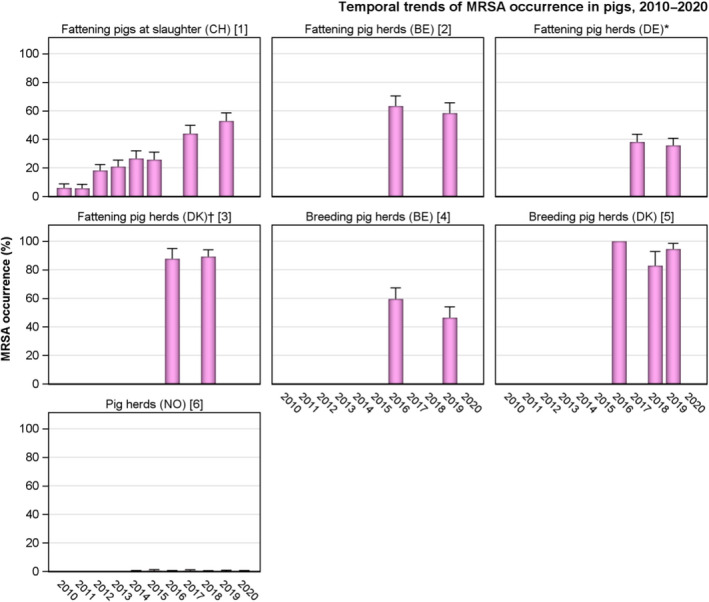
Temporal trends of MRSA prevalence in pigs, 2010–2020
-
BE: Belgium; CH: Switzerland; DE: Germany; DK: Denmark; NO: Norway.Note: The 2‐S method of isolation was used by Belgium and Germany from 2016 to 2019, as well as by Denmark in 2016, in Switzerland from 2010 to 2017 and in Norway from 2014 to 2017. The 1‐S method was used by Switzerland since 2019 and by Denmark and Norway since 2018.*: spa‐types not reported.†: Prevalence data for fattening pig herds (not raised under controlled housing conditions) from 2018 are not included.[1] In 2010, spa‐types: t034 ST398 (17 isolates), t011 ST398 (1), t208 ST49 (5). In 2011, spa‐types: t034 ST398 (19 isolates), t011 ST398 (1), t208 ST49 (1), t2279 ST1 (1). In 2012, spa‐types: t034 CC398 (61 isolates), t011 CC398 (9), t208 ST49 (2). In 2013, spa‐types: t034 (63 isolates), t011 (10). In 2014, spa‐types: t034 (57 isolates), t011 (19), t208 (1), t899 (1), t2741 (1). In 2015, spa‐types: t034 (48 isolates), t011 (23), t032 (1), t571 (1), t899 (1), t1145 (1), t1250 (1), t4475 (1). In 2017, spa‐types: t034 (63 isolates), t011 (61), t899 (2), t1451 (3), t2330 (1), t2876 (1). In 2019, spa‐types were not reported; however, 159/160 isolates were confirmed to belong to CC398 using the sau1‐hsdS1 CC398 PCR reaction (Stegger et al., 2011). The remaining isolate did not survive cryo‐conservation, therefore typing could not be performed.[2] In 2016, spa‐types: t011 CC398 (71 isolates), t1451 (1), t1456 (1), t1456 CC398 (1), t1580 (5), t1985 (8), t1985 CC398 (3), t034 (7), t034 CC398 (2), t037 (1), t898 (1), unspecified (11). In 2019, spa‐types: t011 CC398 (67 isolates), t034 CC398 (11), t1451 CC398 (2), t1457 CC398 (1), t2346 CC398 (1), t2370 CC398 (2), t2383 CC398 (1), t3041 CC398 (1), t3119 CC398 (1), unspecified (18).[3] In 2016, spa‐types not reported. In 2018, spa‐types: t011 CC398 (22 isolates), t034 CC398 (85), t571 CC398 (3), t898 CC398 (1), t2383 CC398 (1), t2974 CC398 (1), t3423 CC398 (1), t4652 CC398 (1), t9266 CC398 (1).[4] In 2016, spa‐types: t011 CC398 (55 isolates), t1451 (2), t1456 (1), t1456 CC398 (3), t1580 (1), t1985 (5), t1985 CC398 (1), t034 (1), t034 CC398 (4), t4659 CC398 (1), unspecified (17). In 2019, spa‐types: t011 CC398 (57 isolates), t034 CC398 (18), t108 CC398 (2), t779 CC398 (1), t2346 CC398 (1), t2582 CC398 (1), t2922 CC398 (1), t3119 CC398 (2).[5] In 2016, spa‐types not reported. In 2018, spa‐types: t011 CC398 (6 isolates), t034 CC398 (24), t1250 CC398 (2), t1793 CC398 (1), t3171 CC398 (1). In 2019, spa‐types t011 CC398 (10), t034 CC398 (57), t1928 CC398 (1), t4652 CC398 (1) were identified in isolates from multiplier pig herds.[6] In 2014, spa‐type: t011 CC398 (1). In 2015, spa‐type: t034 CC398 (2), t177 CC1 (2). In 2016, spa‐type: t034 CC398 (1).In 2017, spa‐types: t091 CC7 (1 isolate), t843 CC130 (1), t6292 CC425 (1). The t091 isolate was PVL‐negative, spa‐types t843 and t6292 were confirmed to carry the mecC gene. In 2019, spa‐type: t034 CC398 (1).
