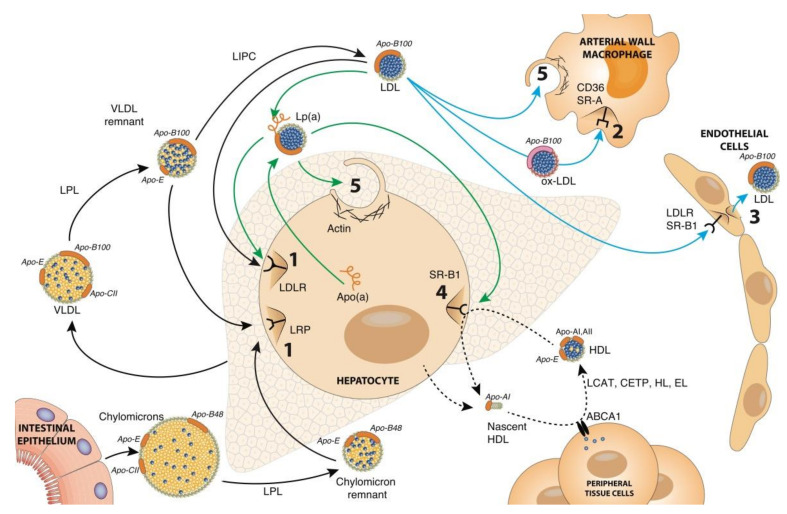
Figure 2.
An overview of lipoprotein endocytosis pathways. Chylomicrons, assembled in the intestine from the absorption of dietary fat, are secreted into circulation where they are acted upon by lipoprotein lipase (LPL) activated by apo-CII to hydrolyse triacylglycerols. The released fatty acids are taken up by peripheral tissues and the resulting chylomicron remnant particles are taken up by hepatocytes through receptor-mediated endocytosis via an interaction with apo-E and the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP). Similarly, VLDL secreted by hepatocytes, also undergoes hydrolysis by LPL to form VLDL remnant particles, some of which are further hydrolysed by hepatic lipase (LIPC) to form LDL. The LDL particles are taken up by hepatocytes through receptor-mediated endocytosis via the low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) binding to apo-B100. Native LDL can also undergo transcytosis in endothelial cells mediated by the SR-B1 receptor. Oxidised LDL (ox-LDL), which arises from oxidative modifications of native LDL, can be endocytosed by arterial wall macrophages either via CD36 or SR-A receptors. Macropinocytosis of native LDL particles by macrophages has also been shown to occur in a receptor-independent manner. LDL particles can form Lp(a) through disulphide bond formation between the apo-B100 and apolipoprotein(a) [apo(a)] components. Lp(a) uptake by hepatocytes can occur through the LDLR or SR-B1 receptor or through macropinocytosis. Nascent high-density lipoproteins (HDL) are secreted from hepatocytes in a lipid-poor state and interact with the ABCA1 transporter on peripheral cells to facilitate lipid transfer and formation of more mature HDL. The HDL molecules then undergo modification by various lipid-modifying enzymes (i.e., LCAT, CETP, HL and EL) and interact with the SR-B1 receptor to selectively transfer accumulated cholesterol esters back to the liver. Black arrows, major lipid transport pathways by apo-B-containing lipoproteins; green arrows, Lp(a) clearance pathways; cyan arrows, alternative LDL uptake pathways; dotted black arrows, HDL. (1) Receptor-mediated endocytosis, holoparticle uptake; (2) receptor-mediated endocytosis, modified holoparticle uptake; (3) transcytosis; (4) receptor-mediated endocytosis, lipid-only uptake; (5) macropinocytosis.