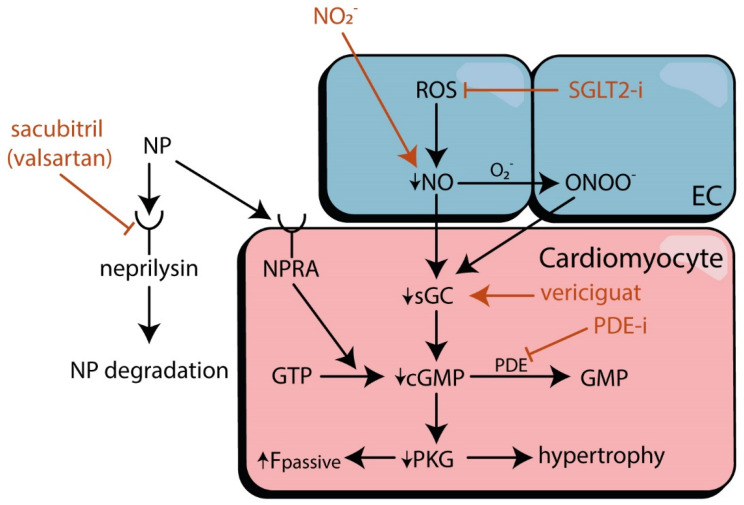
Figure 2.
Interventions targeting MVD in HFpEF. The effects of different pharmacological interventions (blue) on the NO-sGC-cGMP-PKG pathway in MVD in HFpEF. ROS causes impaired NO bio-availability, subsequently disturbing the downstream signalling. The entire pathway offers different targets for therapy. cGMP, Cyclic guanosine monophosphate; EC, endothelial cell; Fpassive, passive force; NO, nitric oxide; NO2−, nitrite; NP, natriuretic peptides; NPRA, Natriuretic peptide Receptor Type A; O2−, superoxide; ONOO−, peroxynitrite; PDE-i, phosphodiesterase inhibitors; PKG, protein kinase G; ROS, reactive oxygen species; sGC, soluble guanylate cyclase; SGLT2-i, sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor; SMC, smooth muscle cell.