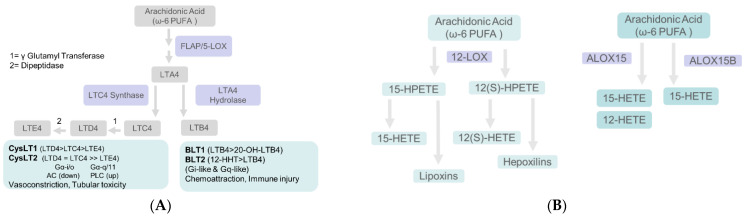
Figure 4.
(A) Schematic showing leukotrienes synthesis and signaling (LOX-5 pathway). Free arachidonic acid (Figure 2) is converted into LTA4 by 5-LOX by activating protein (FLAP). LTA4 is converted into LTB4 by LTA4 hydrolase or LTC4 by LTC4 synthase. Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase attaches glutathione to LTC4 and generates LTD4. A dipeptidase activity converts LTD4 into LTE4. Box under LTB4 shows its G-protein-coupled receptors BLT1 and BLT2 and ligand preferences and LTB4 functions. The text box under cysteinyl leukotrienes LTC4, LYD4 and LTE4 indicates receptors CysLT1 and CysLT2 with ligand preferences. Downregulation (down) of adenyl cyclase (AC) upregulation (up) of phospholipase C (PLC) coupled to specific G proteins is indicated followed by the cellular effects of cysteinyl LTs. (B). LOX-12 and LOX-15 pathways: Left: Arachidonic acid is metabolized by 12-LOX to 15-hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid/arachidonic acid 15-hydroperoxide (15-HPETE/15-HpETE) or 12(S)-HPETE/12-HPETE. 15-HPETE is further metabolized to yield 15-HETE and lipoxins (specialized pro-resolving mediators). 12-HPETE generates 12-HETE and hepoxilins (anti-inflammatory). Right: Lipoygenase-15 (ALOX15) and ALOX15B generate 15-HETE as the dominant product with a small amount of 12-HETE by ALOX15 activity.