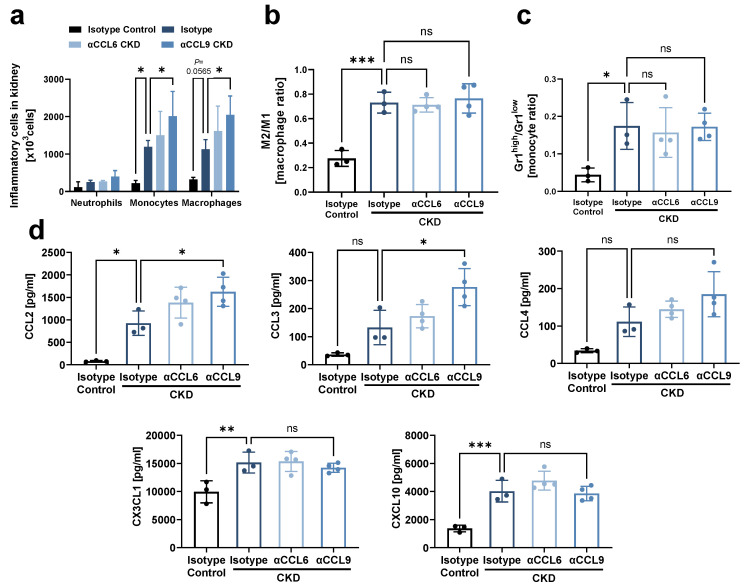
Figure 3.
Systemic antibody-mediated blocking of CCL9 increases kidney inflammation. As in Figure 2a, hyperlipidemic ApoE−/− mice with adenine-induced CKD were treated with blocking antibodies against CCL6 (αCCL6 CKD) or CCL9 (αCCL9 CKD), or with isotype-matched antibody controls (Isotype CKD) (n = 3–4). Hyperlipidemic ApoE−/− mice without adenine but with isotype-matched antibody treatment served as non-CKD controls (Isotype Control). (a) Flow cytometric analysis of neutrophils, monocytes and macrophages in kidney. (b,c) The ratio of (b) M2 vs. M1 macrophages and (c) Ly-6Ghigh vs. Ly-6Glow monocytes in kidney by flow cytometric analysis. (d) Chemokine concentration in kidney analyzed using a LUNARIS assay. (a–d) Two-way ANOVA (a) or one-way ANOVA (b–d) with Dunnett’s post-test for multiple comparisons. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, ns = not significant.