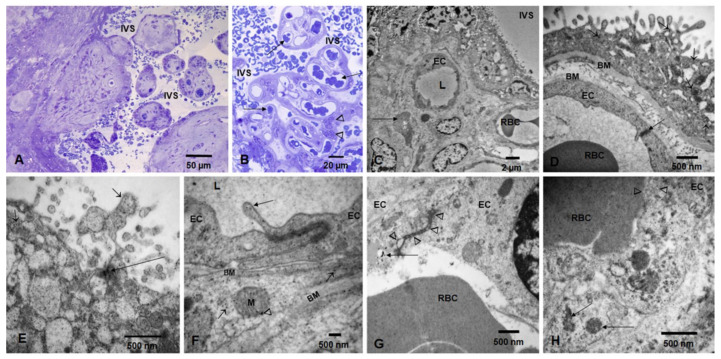
Figure 2.
Toluidine blue 1 um thick sections and TEM in term placentas. Toluidine blue 1 um thick sections showing term villi surrounded by intervillous space (IVS) occupied by maternal RBC (A). Thin syncytiotrophoblast and numerous blood vessels (long arrows) occupied by fetal RBC and Hofbauer cells (arrowheads) are seen in (B). Electron micrograph showing the IVS, syncytiotrophoblast, fetal blood vessels, endothelial cells (EC) with luminal (L) RBC, and a Hofbauer cell (long arrow) (C,D). A close-up of a villous shows the syncytiotrophoblast layer resting on a basement membrane (BM upper) with numerous NPs (short arrows). A fetal endothelial cell (EC) contains a fetal RBC, and an intact EC tight junction is seen (long arrow) (E). Close up of syncytiotrophoblast with numerous free NPs (short arrows) and clusters of NPs (long arrows). (F). Fetal blood vessel with two ECs and a tight junction (TJ). Note the prolongation into the lumen (L) of the endothelial cell containing NPs (long arrow). The EC is resting on a basement membrane (BM upper). A pericyte surrounds the ECs and contains cytoplasmic free NPs (short arrows) and NPs in mitochondria (arrowhead). The pericyte basement membrane is visible (BM lower). (G). Fetal ECs with an abnormal TJ (arrowheads), occupied by NPs and an adjacent EC lysosome, contains numerous NPs (long arrow). The fetal RBC is seen in vessel lumen. (H). One fetal luminal RBC in close contact with the EC shows an area of intense caveolar activity (arrowheads) and NPs lining the contact surface. ECs contain numerous lysosomes with NPs (long arrows).