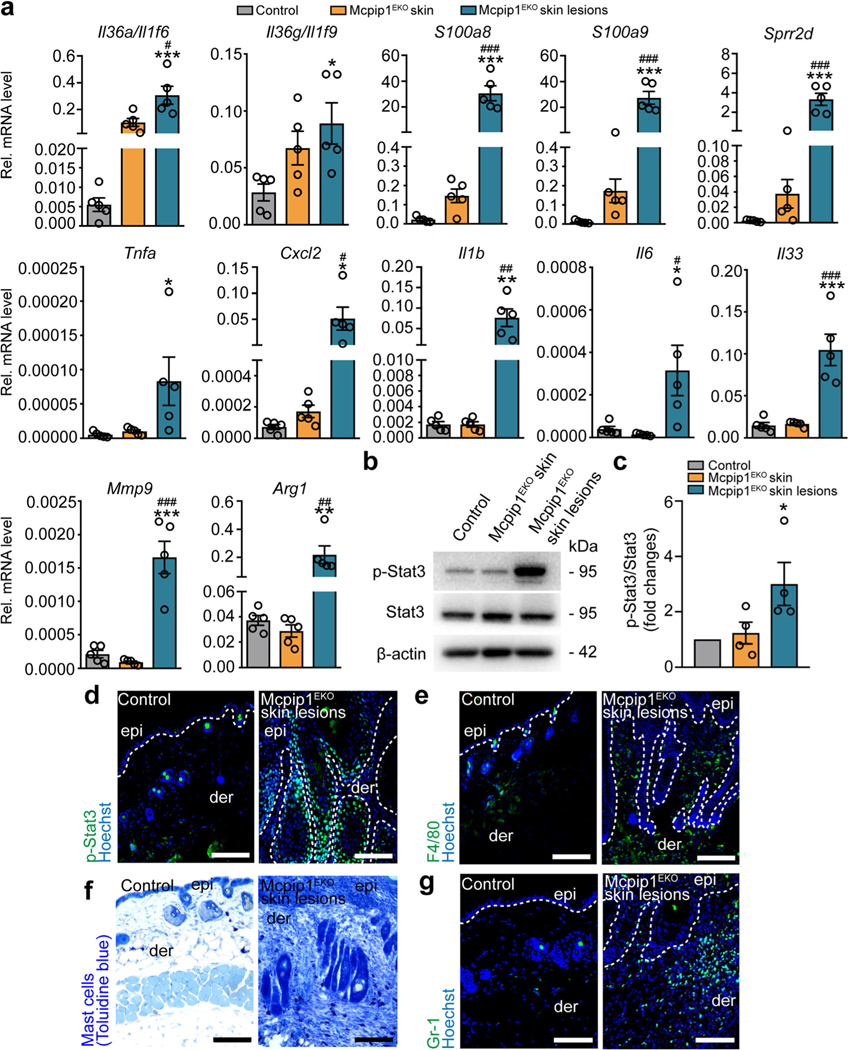
Fig. 6.
Old Mcpip1EKO mice spontaneously develop skin inflammation. a QRT-PCR analysis of Il36a/Il1f6, Il36g/Il1f9, S100a8, S100a9, Sprr2d, Tnfa, Cxcl2, Il1b, Il6, Il33, Mmp9, and Arg1 transcript levels in the healthy skin of the control and Mcpip1EKO mice (6–8 mo) and in the skin lesions of Mcpip1EKO mice (n = 5). b Representative Western blot for p-Stat3, Stat3, and β-actin in the control and Mcpip1EKO mice (6–8 mo) from four independent experiments. c Densitometric quantification of p-Stat3/Stat3 levels (n = 4). d P-Stat3 immunofluorescence staining of the skin sections. e F4/80 immunostaining. f Toluidine blue immunostaining. g Gr-1 immunostaining. Scale bar, 100 μm. Data represent the mean ± SEM; epi, epidermis; der, dermis. The dashed line indicates the basal membrane. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA. * refers to the comparison of control and Mcpip1EKO skin lesions; # refers to the comparison of Mcpip1EKO skin and Mcpip1EKO skin lesions