Figure 1.
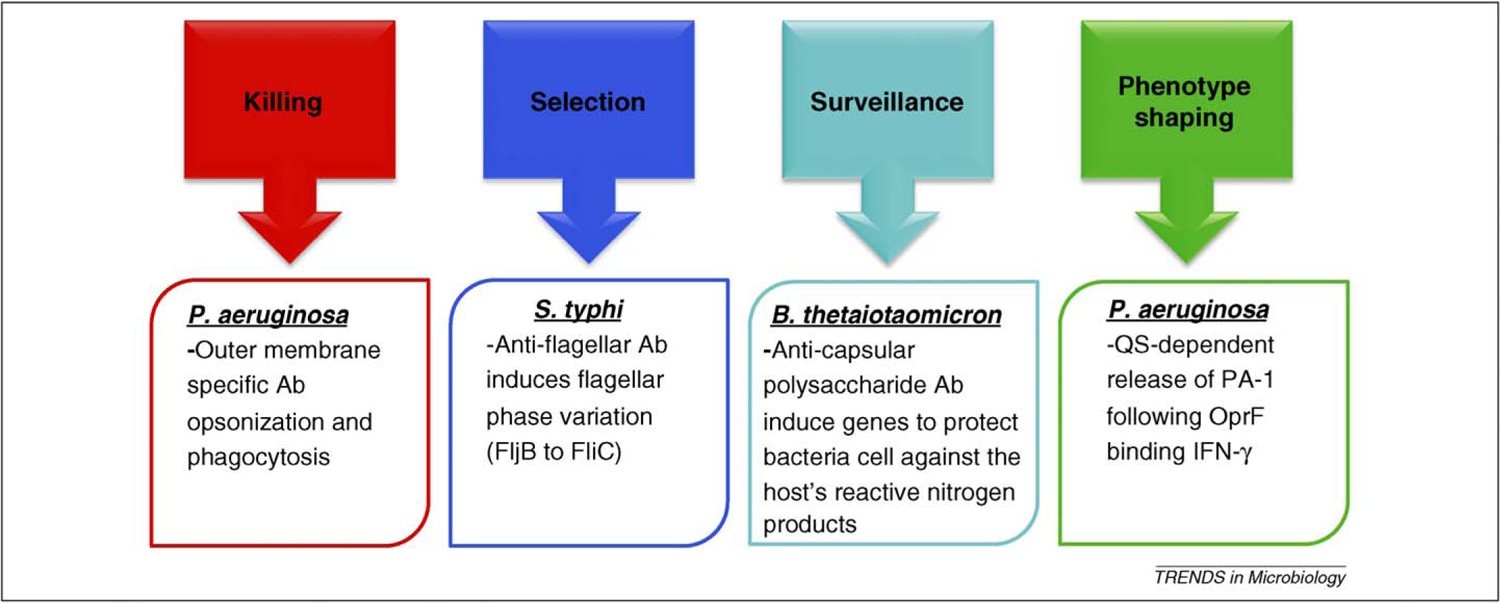
OM structure-specific antibodies and IE mediate diverse outcomes following interaction with bacteria. Killing: multiple OM structures (LPS, porins, capsule) can be bound by antibodies that interact with Fc receptors on phagocytes for effective killing of bacteria. Selection: antibodies to S. typhi flagella [24] result in selection of variants or induction of phase variation to change antibody targets. Surveillance: commensal bacteria can survey the lumen and respond to anti-LPS antibodies by expression of genes associated with protection from the host’s innate immune defenses [32]. Phenotype shaping: new evidence and extension of other observations suggest that antibodies and IE can regulate bacterial phenotypes. This could be via direct receptor–IE interaction (IFN-γ [18]) or indirectly by antibodies, for example, by preventing function of OM proteins (Opr86) and thus the cell adjusting gene expression for the perceived loss of general functions [48].
