FIGURE 1.
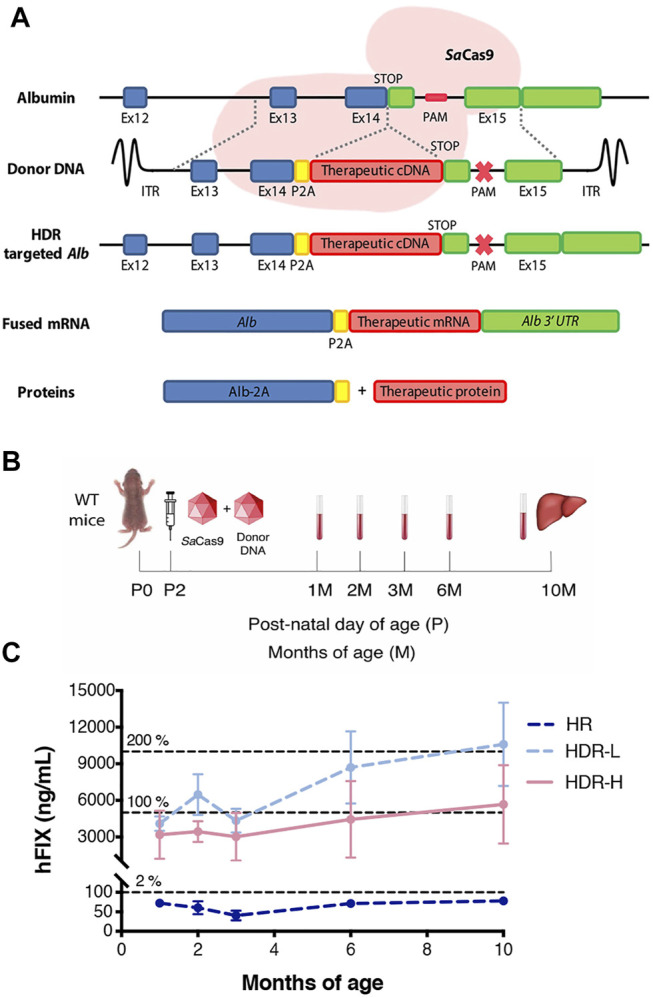
In vivo gene targeting of hFIX into the albumin locus in neonatal wild-type mice. (A) Targeting strategy for integration of donor hFIX cDNA vector, proceeded by the 2A-peptide and flanked with arms of homology for the albumin locus. Albumin and hFIX are transcribed into a single hybrid mRNA molecule and translated into two separate proteins. The CRISPR/SaCas9 performs a double-strand break in the intron located downstream of the albumin stop codon, enhancing the homologous directed repair rate; (B) Experimental scheme. Wild-type mice were i.v. injected at post-natal day 2 with only rAAV8-donor-hFIX (2.0E11 vg/mouse, HR, n = 5) or with rAAV8-donor-hFIX combined to different rAAV8-SaCas9-sgRNA8 doses (6.0E10 vg/mouse, HDR L, n = 5; or 2.0E11 vg/mouse, HDR H, n = 5). Blood was collected at different time points and mice were sacrificed at 10 months of age; (C) Plasma hFIX levels were evaluated at 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 10 months of age. The dotted lines at 5,000 ng/ml and 10,000 ng/ml represent 100 and 200%, respectively, of the hFIX levels present in the healthy human population. Values are represented with mean ± SD. Two-way ANOVA (Bonferroni test) Interaction ns (p = 0.1356), Treatment *** (p < 0.0001), Time ** (p = 0.0074).
