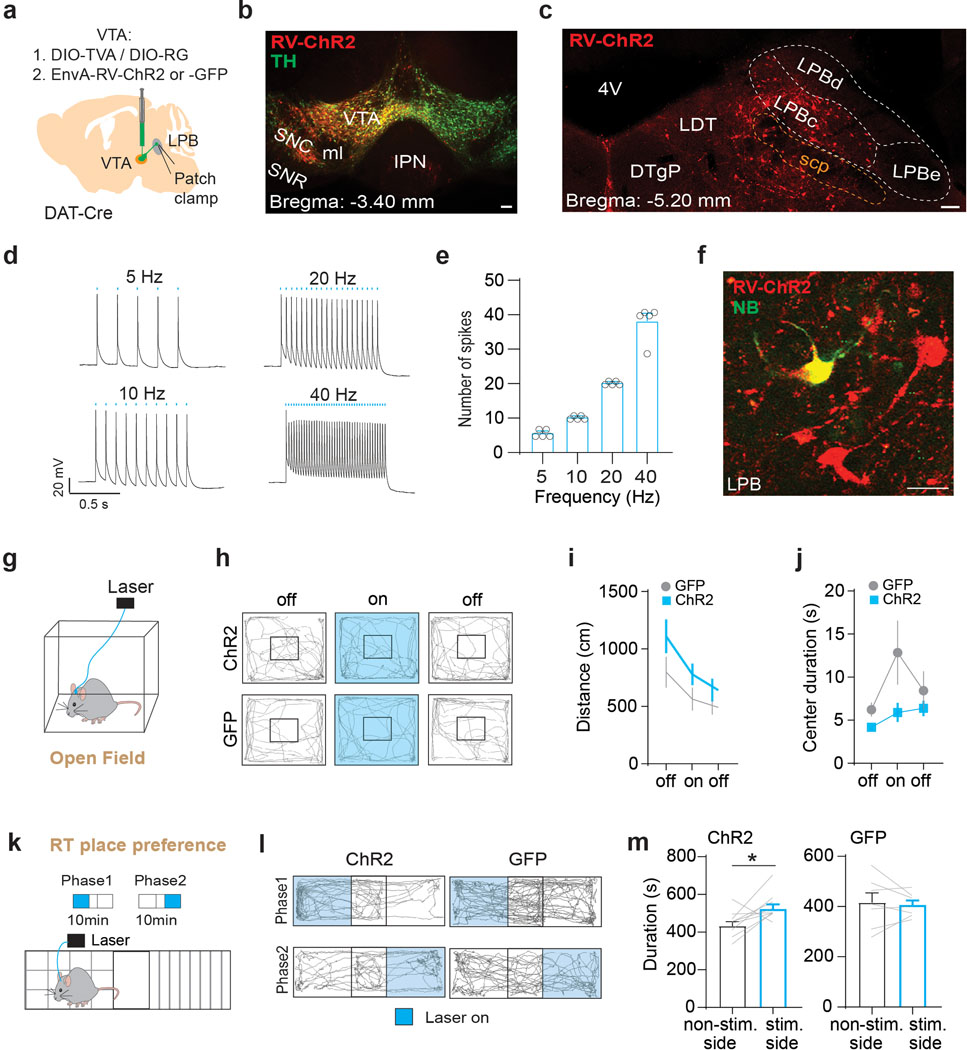
Extended Data Fig. 10. Optogenetic stimulation of LPB→VTA DA neurons does not affect locomotor activity but promotes reward-related behavior.
(a) Targeting of AAVs encoding the cellular receptor for subgroup A avian leukosis viruses (TVA) and rabies virus glycoprotein (RG) as well as EnvA-pseudotyped, glycoprotein-deficient rabies virus expressing ChR2 or GFP (EnvA-RV-ChR2/-GFP) to VTA of DAT-Cre mice. Patch-clamp recordings were performed from LPB neurons (d-f) or bilateral optical fibers were implanted above the LPB for assessment of locomotor activity in open field test (g-j). (b) Injection site in VTA (scale bar 100 μm). (c) ChR2-expressing cells in LPB, which make monosynaptic connections onto VTA DA neurons (scale bar 100 μm). (d) Sample patch-clamp recordings from LPB neurons showing light-evoked action potentials in response to 5 Hz, 10 Hz, 20 Hz or 40 Hz stimulation (scale bars 20 mV/0.5 sec). (e) Mean number of spikes in response to different stimulation frequencies (5 Hz: n = 5 cells, 10 Hz: n = 5 cells, 20 Hz: n = 5 cells, 40 Hz: n = 5 cells). (f) Neurobiotin (NB)-filled LPB cell expressing ChR2 (scale bar 20 μm). (g) Experimental design. (h) Representative trajectories of animals expressing ChR2 (top) or GFP (bottom) in LPB→VTA DA neurons. (i) 20 Hz stimulation of LPB→VTA DA neurons does not have significant effect on the mean distance traveled between ChR2- (left) and GFP-expressing (right) mice. (j) No significant difference in time spent in center area between ChR2 and GFP mice. (k) Schematic of real-time (RT) place preference assay. (l) Trajectories of sample ChR2- and GFP-expressing mice during RT place preference test. (m) ChR2- (left) but not GFP-expressing (right) mice spent significantly more time on the side of the chamber paired with light stimulation of LPB→VTA DA neurons (ChR2: n = 9 mice, GFP: n = 7 mice). Data represent mean ± SEM. Significance was calculated by means of one-way RM ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test (i) and two-way RM ANOVA with Holm-Sidak’s post-hoc test (j) or paired t-tests (m). * p < 0.05.