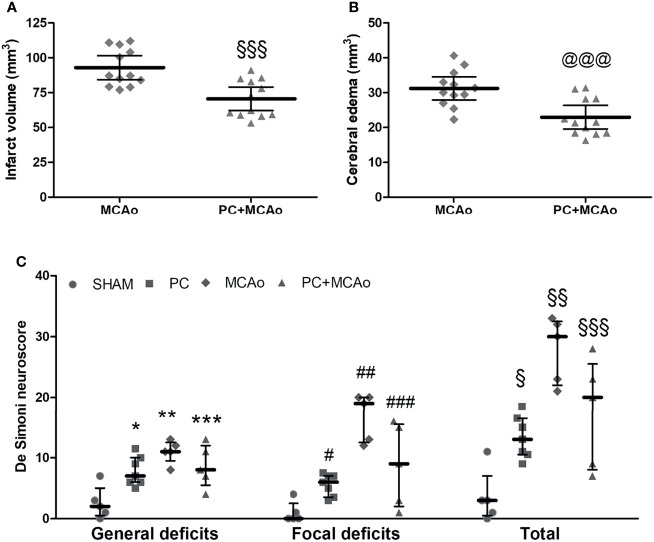
Figure 6.
Ischemic PC significantly reduces brain damage and neurological deficits caused by 1h MCAo. (A) Cerebral infarct volume and (B) brain edema in mice subjected to 1h MCAo followed by 24h of reperfusion preceded 72h before by sham surgery (MCAo) or by ischemic PC (PC+MCAo); §§§P = 0.0005 and @@@P = 0.0009 vs MCAo (unpaired t-test, n = 12 mice per experimental group). (C) General, focal and total deficits caused in mice by SHAM surgery, ischemic PC (15min MCAo, followed by 72h of reperfusion), 1h MCAo followed by 24h of reperfusion (MCAo) or ischemic PC 72h before MCAo (PC+MCAo). Data were analysed by Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Bonferroni’s correction (*P = 0.0227 vs corresponding SHAM, **P = 0.0088 vs corresponding SHAM and P = 0.0182 vs corresponding PC, ***P = 0.0212 vs corresponding SHAM, #P = 0.0111 vs corresponding SHAM, ##P = 0.0080 vs corresponding SHAM and P = 0.0044 vs corresponding PC, ###P = 0.0339 vs corresponding SHAM, §P = 0.0145 vs corresponding SHAM, §§P = 0.0088 vs corresponding SHAM and P = 0.0045 vs corresponding PC, §§§P = 0.0278 vs corresponding SHAM; n = 5-7 mice per experimental group).