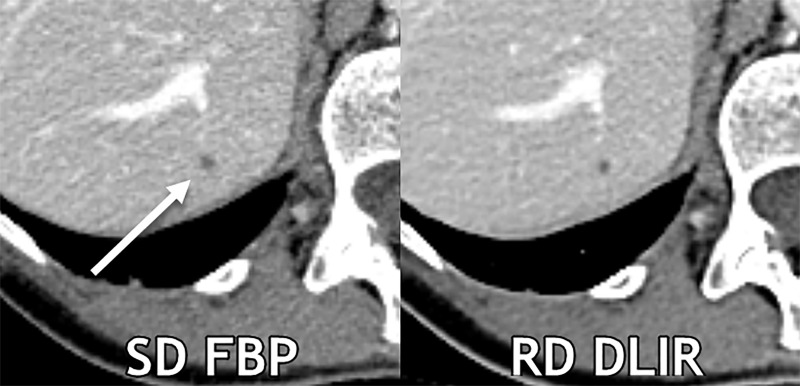
Figure 4:
Axial contrast-enhanced CT images show a 0.3-cm liver cyst (arrow) that was detected by all readers on both scans. However, all three reader characterizations were false-positive at standard-dose (SD) filtered back projection (FBP), whereas the regular-dose (RD) deep learning image reconstruction (DLIR) with medium strength scan resulted in two true-negative characterizations and one false-positive characterization. At a radiation dose reduction of 66% on this scan, the cyst appears more conspicuous with DLIR, and each reader qualitatively scored the reduced-dose DLIR scan to be better than or equivalent to the standard-dose FBP scan. Contrast-to-noise ratios for liver metastases in this participant for standard-dose FBP and reduced-dose DLIR were 3.9 and 4.6, respectively.