Figure 1.
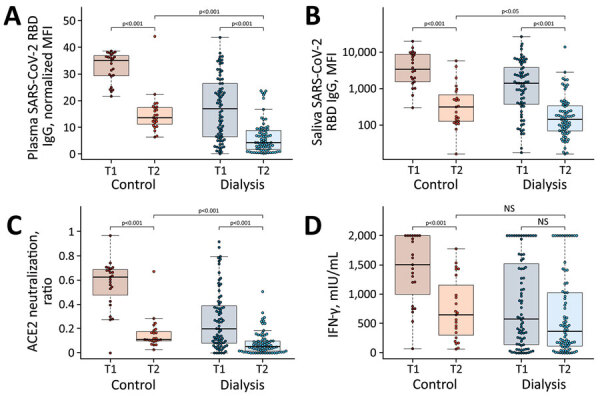
Significant decrease in humoral and cellular responses induced by Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine BNT162b2 (https://www.pfizer.com) against SARS-CoV-2 from 3 weeks to 16 weeks after second vaccination, observed in a study of immune response against variants of concern in dialysis patients 4 months after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination. A) IgG response in plasma; B) IgG response in saliva; C) neutralizing capacity toward SARS-CoV-2 wild type B.1; D) T-cell response measured by IFN-γ release assay. Blue circles indicate dialysis patients (n = 76) and red circles controls (n = 23). Samples were taken 3 weeks (T1) and 16 weeks (T2) after vaccination. Saliva (panel B) has reduced sample numbers in both groups because of issues in sample collection (T1 control, n = 22; T1 dialysis, n = 69; T2 control, n = 23; T2 dialysis. n = 71). T1 timepoint data has been published previously (13) and is reproduced here for clarity. Horizontal lines within boxes indicate medians; box tops and bottoms indicate the 25th and 75th percentiles; whiskers show the largest and smallest nonoutlier values. Outliers were determined by 1.5 times interquartile range. Statistical significance was calculated by Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test when comparing T1 and T, and 2-sided Mann–Whitney–U test when comparing control and dialysis groups. ACE2, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; IFN-γ, interferon γ; MFI; median fluorescence intensity; NS, not significant; RBD, receptor-binding domain; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; T1, timepoint 1; T2, timepoint 2.
