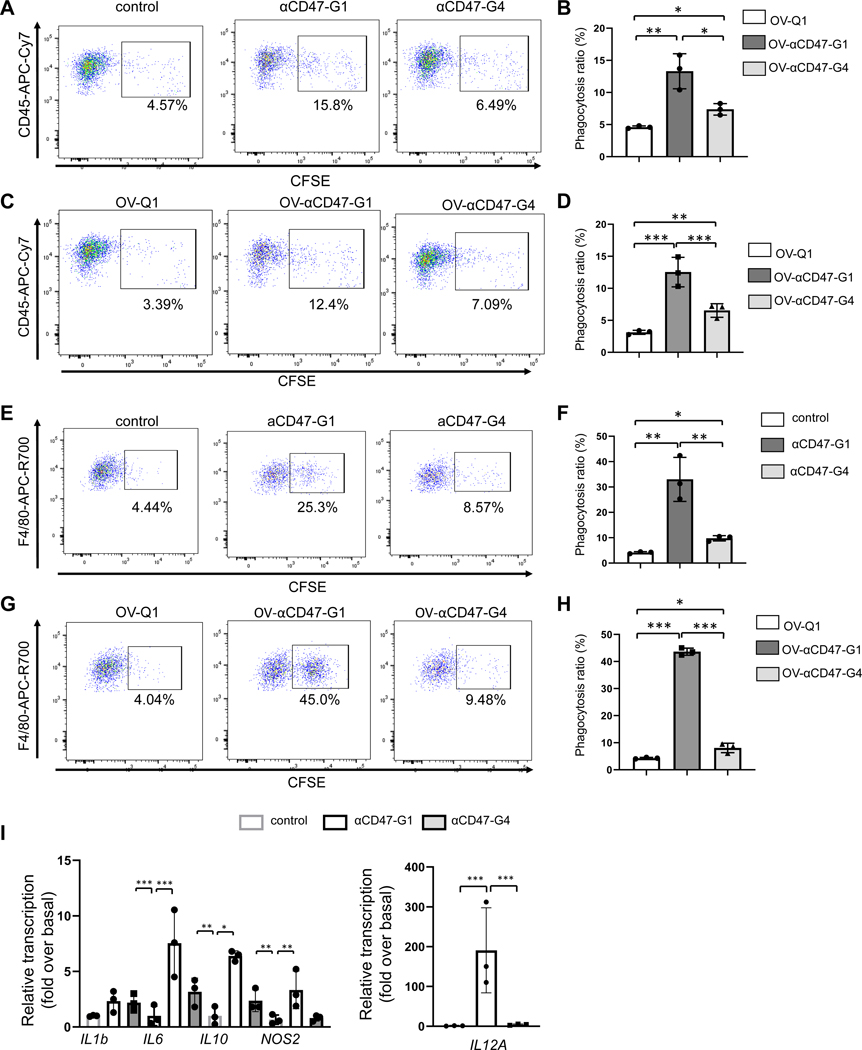
Figure 2. αCD47-G1 and αCD47-G4 induce phagocytosis of A2780 ovarian cells by macrophages.
(A-B) Examination of the effect of 5 μg/ml of αCD47-G1 and αCD47-G4 purified from lentiviral- infected CHO cells on phagocytosis of A2780 cells by primary human macrophages. (C-D) The supernatants from OV-αCD47-G1- and OV-αCD47-G4-infected A2780 cells induce phagocytosis against A2780 cells by primary human macrophages. Phagocytosis was assessed by flow cytometry. (E-F) Examination of the effect of 5 μg/ml of αCD47-G1 and αCD47-G4 purified from lentiviral-infected CHO cells on phagocytosis of A2780 cells by bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs). Percentages of BMDM phagocytosis of A2780 cells (CD11b+CFSE+) were determined by flow cytometry. (G-H) The supernatant from OV-αCD47-G1- and OV-αCD47-G4-infected A2780 cells induce phagocytosis against A2780 cells by BMDMs. Phagocytosis was assessed by flow cytometry. (I) Primary human macrophages were cocultured with A2780 cells at a ratio of 1:1 with or without αCD47-G1 or αCD47-G4 for 6 hours after which gene transcripts were quantified. All experiments were repeated using 3 human donors or mice with similar results. Statistical analyses were performed by one-way ANOVA with P values corrected for multiple comparisons by Bonferroni method. *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001. Data were presented as mean values +/− SD.