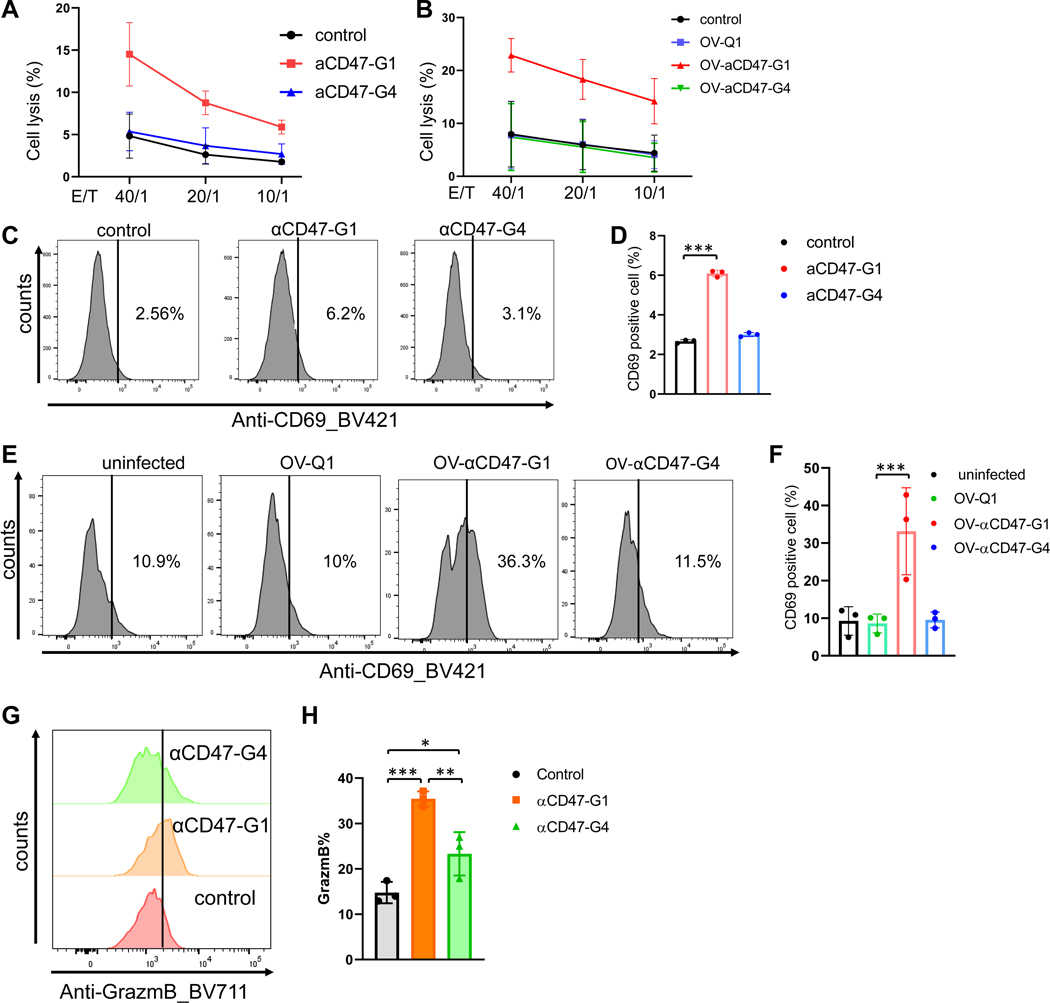
Figure 3. αCD47-G1 but not αCD47-G4 induces cytotoxicity of human NK cells against ovarian cancer cells.
(A) Cytotoxicity of human primary NK cells against αCD47-G1- and αCD47-G4-treated A2780 human ovarian cancer cells. PBS was the control. Control vs. αCD47-G1 ***P ≤ 0.001; αCD47-G1 vs. αCD47-G4 *P ≤ 0.05. (B) Cytotoxicity of human primary NK cells against A2780 cells that were treated with supernatants from OV-Q1-, OV-αCD47-G1- or OV-αCD47-G4-infected A2780 cells. OV-Q1 vs. OV-αCD47-G1, ***P ≤ 0.001; OV-αCD47-G1 vs. OV-αCD47-G4, ***P ≤ 0.001. (C) CD69 expression of NK cells cocultured with A2780 cells that were pretreated with αCD47-G1 or αCD47-G4 was detected by flow cytometry. (D) Summary data of (C). (E) CD69 expression of NK cells when cocultured with A2780 cells with supernatants from OV-Q1-, OV-αCD47-G1- or OV-αCD47-G4-infected A2780 cells was detected by flow cytometry. (F) Summary data of (E). (G) Granzyme B expression by NK cells cocultured with A2780 cells that were pretreated with αCD47-G1 or αCD47-G4 was detected by flow cytometry. (H) Summary data of (G). All experiments were performed with three donors. Error bars represent standard deviations of the means of three donors. For C to H, statistical analyses were performed by one-way ANOVA with P values corrected for multiple comparisons by Bonferroni method. *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001. Data were presented as mean values +/− SD.