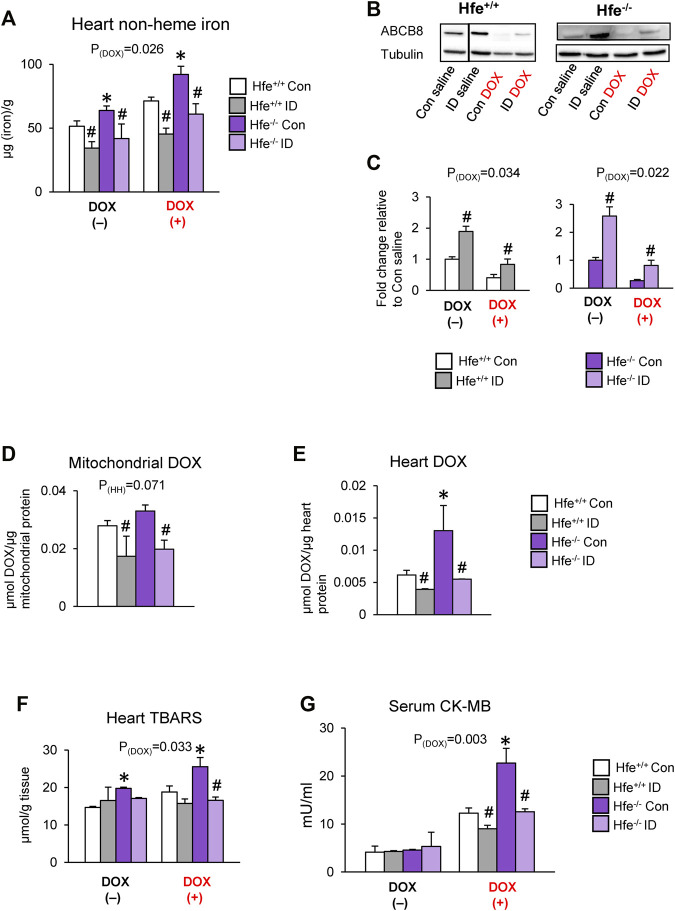
FIGURE 6.
Correcting iron overload prevents exacerbated DOX cardiotoxicity in HH. Hfe+/+ and Hfe−/− mice were maintained on iron-deficient (ID) diet and administered DOX (20 mg/kg) as described in the Methods section. Cardiac non-heme iron levels were measured by colorimetric assay using bathophenanthroline disulfonate (A). ABCB8 levels in the heart were measured by western blot analysis and normalized to levels of α-tubulin (B,C). Discontinuities between non-adjacent lanes of the same membrane were indicated by a solid line. Mitochondrial (D) and cardiac (E) DOX levels were measured in cardiac tissue by fluorescence and normalized to protein content. Oxidative stress was determined as TBARS levels and measured by colorimetric assay (F). Serum CK-MB levels were measured by ELISA (G). Results are representative of n = 7,8/group except (B) where n = 4,5/group. Data were expressed as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was assessed using ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc comparisons. *p < .05 vs. Hfe+/+ of the same treatment. # p < .05 vs. control diet of the same genotype.