FIGURE 2.
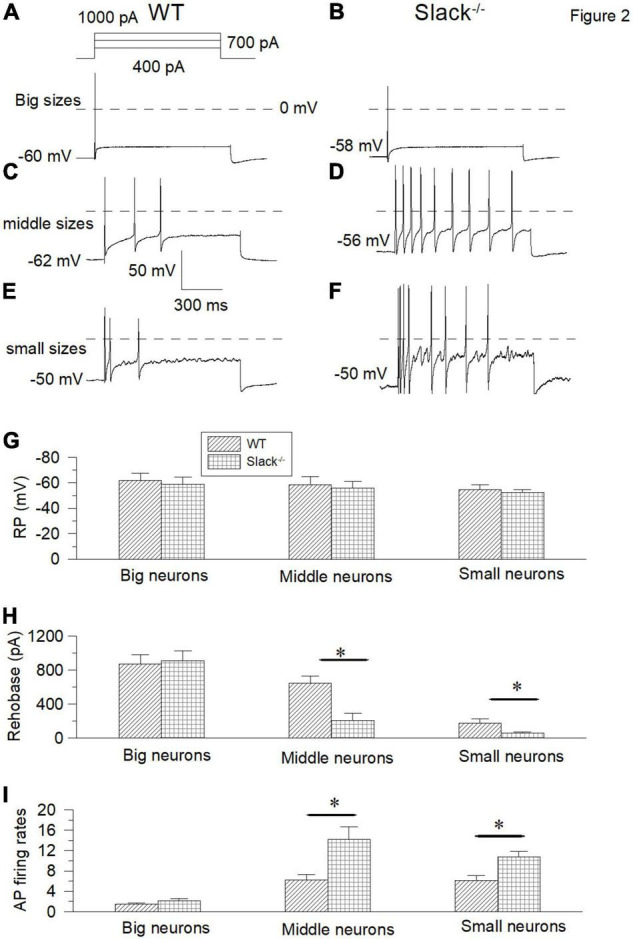
The small and middle-sized DRG neurons in the Slack–/– mice exhibit overactivity. (A,B) Sample action potential traces of the big-sized DRG neurons in the WT and Slack–/– mice were elicited by 1000 pA current injection. (C,D) The action potential traces of the middle-sized DRG neurons were elicited by 700 pA current injection. (E,F) Sample action potential traces of small-sized DRG neurons in the WT and Slack–/– mice were elicited by 400 pA current injection. (G) Comparison of resting membrane potentials of the big-sized (WT, n = 10, Slack–/–, n = 10, Student T-test, P = 0.51), middle-sized (WT, n = 11, Slack–/–, n = 11, P = 0.64) and small-sized (WT, n = 11, Slack–/–, n = 11; P = 0.7) DRG neurons in the WT mice and Slack–/– mice, respectively. (H) Comparison of rheobase currents in the big-sized (WT, n = 11; Slack–/–, n = 11; P = 0.63), middle-sized (WT, n = 11; Slack–/–, n = 11; P = 0.01) and small-sized (WT, n = 11; Slack–/–, n = 11; P = 0.005) DRG neurons in the WT mice and Slack–/– mice, respectively. (I) Comparison of action potential firing rates of the big-sized (WT, n = 8; Slack–/–, n = 8; P = 0.61), middle-sized (WT, n = 10; Slack–/–, n = 10; P = 0.014) and small-sized (WT, n = 12; Slack–/–, n = 12; P = 0.012) DRG neurons in the WT mice and Slack–/– mice, respectively. *P < 0.05.
