Figure 1. Post–bisulfite conversion library preparation methods for WGBS.
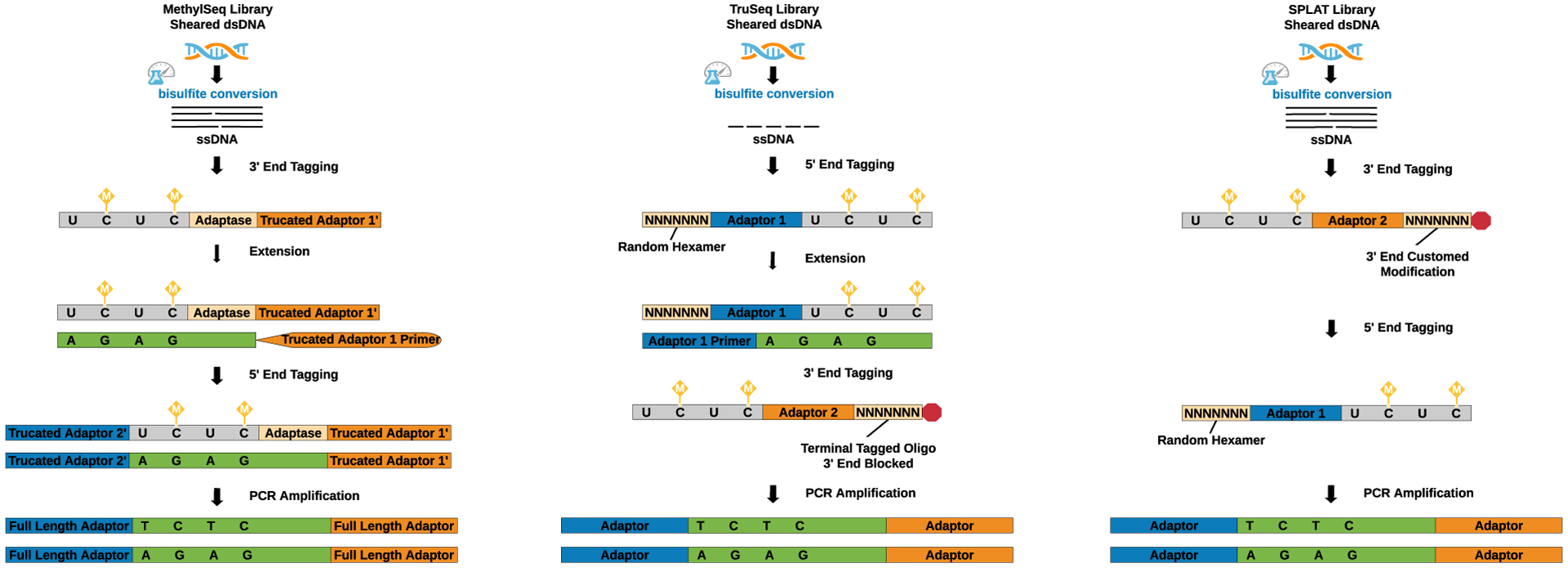
(1) The Accel-NGS® Methyl-Seq kit (Accel) uses pre-sheared bisulfite-treated single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) as a template that is selectively tagged with a low complexity sequence tail and an adapter sequence at the 3’ end with Adaptase™ technology. After extension, a second specific sequence tag with adapters is ligated. The di-tagged DNA is amplified by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) resulting in double-strand DNA (ds DNA). (2) The TruSeq kit (Illumina) uses ssDNA as a template, which is simultaneously randomly primed and attached with a 5’ end adapter sequence by random hexameric oligonucleotides. Subsequently, a 3’ end adapter is tagged by the random sequence oligonucleotide with the 3’ end blocked to prevent adapter self-ligation. Finally, the di-tagged TruSeq libraries are PCR amplified resulting in dsDNA. (3) The SPLAT (SPlinted ligation adapter tagging) method uses pre-sheared ssDNA as a template that is attached with an adapter sequence and a protruding random hexamer (3’ end blocked) at the 3’ end. Thereafter, an adapter with a random hexamer is annealed to the 5’ end. Finally, the di-tagged SPLAT libraries are PCR amplified to produce dsDNA.
