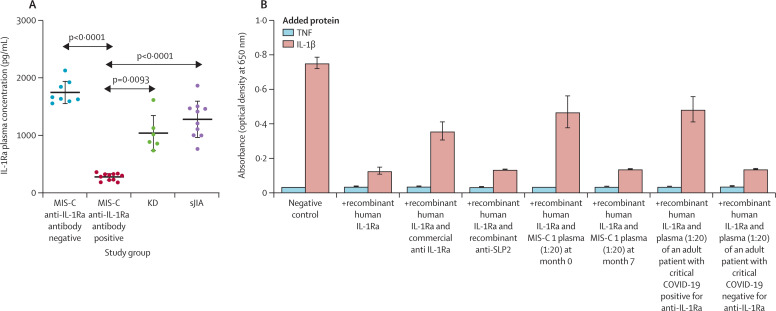
Figure 2.
Neutralising and functional effect of anti-IL-1Ra antibodies in MIS-C
(A) Free IL-1Ra plasma concentrations as measured by ELISA in patients with MIS-C (n=21), Kawasaki disease (n=6) and systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (n=10). Horizontal lines represent the mean and SD. Data were analysed by Brown–Forsythe and Welch ANOVA with Dunnett's T3 multiple comparisons. (B) IL-1β-signalling reporter assay on selected MIS-C plasma compared with an adult critical COVID-19 plasma sample (both 1:20 dilution) as well as commercially available anti-IL-1Ra antibody or control (anti-SLP2) antibody. The absorbance of secreted embryonic alkaline phosphatase, as a marker for IL-1β pathway activation in HEK IL-1β reporter cells, was detected at 650 nm. Error bars show mean (SD). MIS-C=multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children. IL-1Ra=interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. KD=Kawasaki disease. sJIA=systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. TNF=tumour necrosis factor. IL-1β=interleukin-1β.