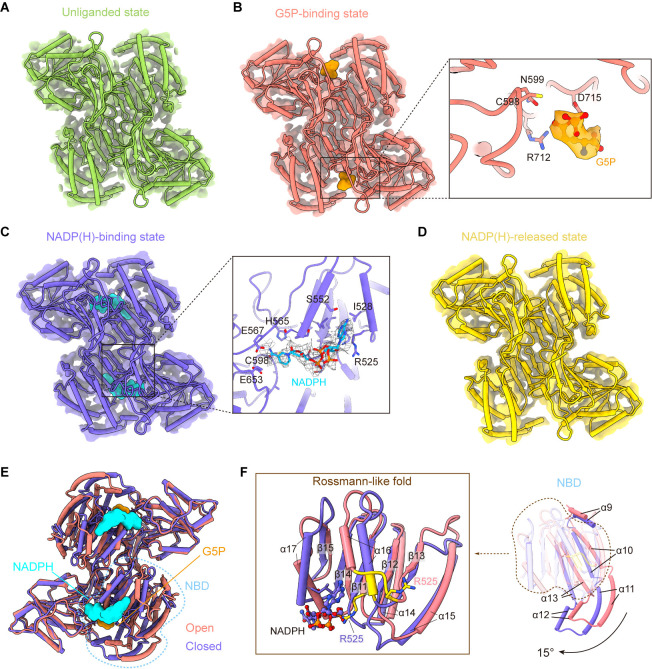
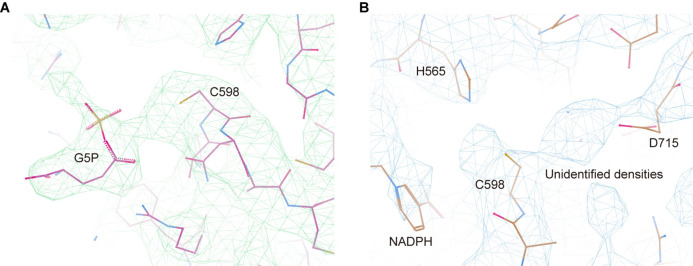
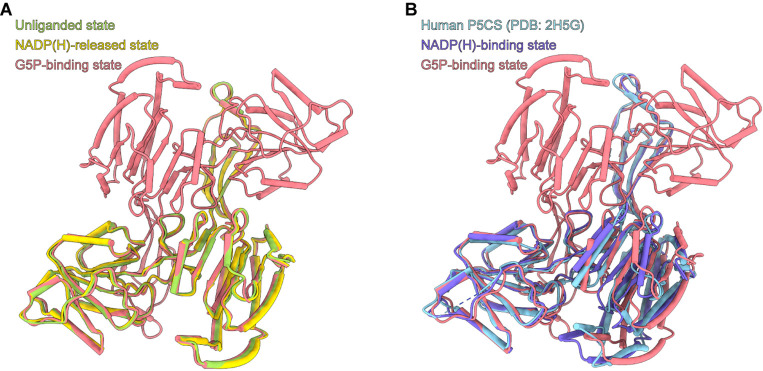
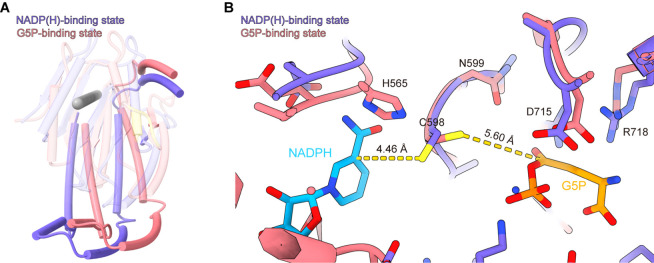
Figure 4. γ-Glutamyl phosphate reductase (GPR) domain ligand-bound mode and its conformation.
(A) The cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) density of the GPR dimer structure and cartoon model is represented as an unliganded state in the P5CSGlu filament (green). (B) GPR dimer structure of the G5P-binding state in the P5CSGlu/ATPγS filament (coral). The conformation of the G5P-binding pocket and G5P (orange) is shown as stick representation. (C) GPR dimer structure of the NADP(H)-binding state in the P5CSMix filament (blue-violet). The conformation of the NADP(H)-binding pocket with NADPH (cyan) is shown as stick representation. (D) GPR dimer structure of the NADP(H)-released state in the P5CSMix filament (yellow). (E) Structural differences in the G5P-binding state (coral) and NADP(H)-binding state (blue-violet) of the GPR domain. Ligands are colored as in (B, C). (F) Superimposition of either the NADPH-binding domain (NBD) or the Rossmann-fold of the GPR domain at the G5P-binding state and NADP(H)-binding state using a single protomer.