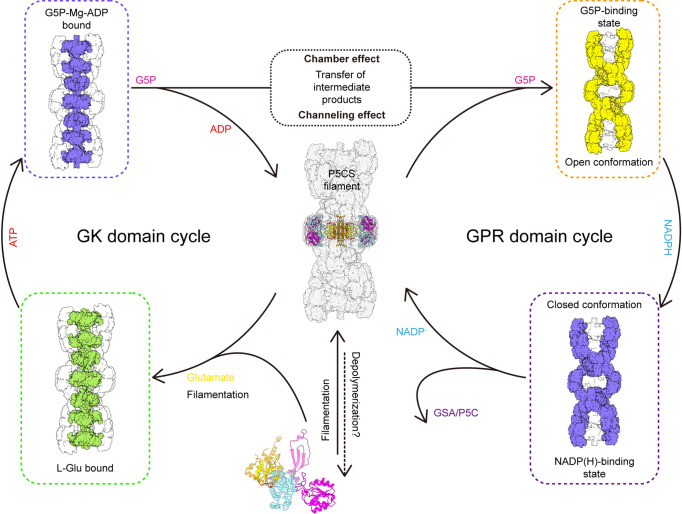
Figure 6. Model of P5CS filament structural transitions during GSA/P5C synthesis.
The P5CS molecule polymerizes into filaments at the APO state or after binding with the glutamate. Upon ATP binding, the glutamate kinase (GK) domain initiates glutamate phosphorylation. The product leaves the pocket, and the GK domain subsequently repeats reaction cycle (left). Unstable G5P will be transported through channel and the half-open chamber inside the filament, and captured by the γ-glutamyl phosphate reductase (GPR) domain. NADPH binding to the GPR domain transforms the domain to closed conformation, which enables NADPH to approach the catalytic site and completes reductive dephosphorylation of G5P. The GSA/P5C will be released, and the GPR domain returns to the unliganded state with open conformation. The GPR domain then begins the next cycle (right).