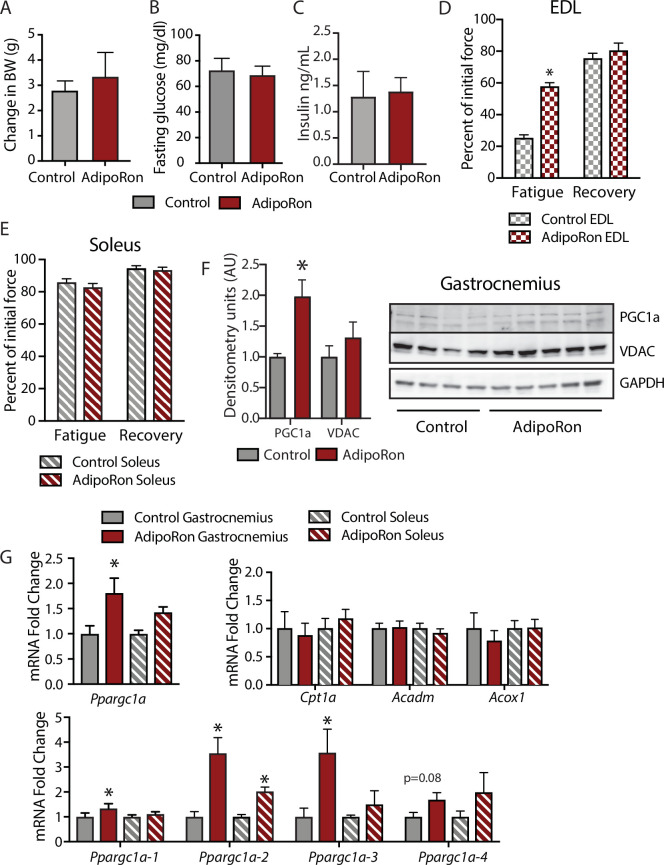
Figure 3. Metabolic and functional effects of chronic AdipoRon treatment in young mice.
Chronic AdipoRon treatment (1.2 mg/kg BW, intravenous injection three times per week for 6 weeks) in young male B6C3F1 mice (3.5 months). Measures of (A) body weight, (B) fasting glucose, (C) fasting insulin (Control [n=5] and AdipoRon [n=5]). Measures of peak force after tetanic stimulation in ex vivo contractility experiments in isolated EDL (D) and Soleus (E) muscles. (F) Immunodetection of protein levels of PGC1a and VDAC in gastrocnemius muscle. (G) mRNA expression of Ppargc1a, PGC-1a gene targets, and Ppargc1a isoforms in gastrocnemius and soleus muscle. Data shown as mean ± SEM, significance determined by Student’s t-test (*p<0.05). EDL, extensor digitorum longus.