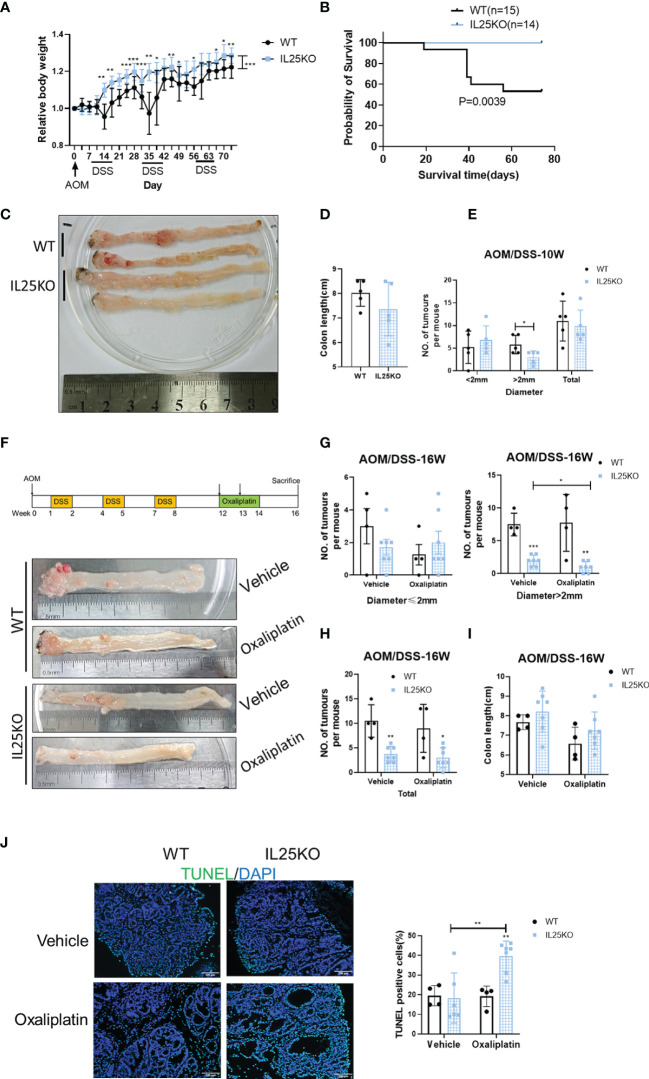
Figure 2.
Genetic deletion of IL25 inhibited the progression of the Colitis-Associated Cancer (CAC) Model. IL25KO or WT control mice were given an intraperitoneal injection of AOM on day 1, 2.5% DSS in drinking water for 7 days starting on days 7, 28, and 42, and euthanized on days 70 and 112. (A) Bodyweight change during colitis-associated colorectal cancer with AOM/DSS as a percentage of initial weight. (B) Overall survival curves of WT and IL25KO mice. (C) Representative images of colonic tumors from WT and IL25KO mice in 10 weeks. (D) Total number and size of tumors along the colon in WT (n = 5) and IL25KO (n = 5). (E) Colon length in mice treated with the indicated treatment in 10 weeks. (F) Effect of oxaliplatin on WT and IL25KO AOM-DSS-induced CRC mouse models. The colon was removed, cut lengthwise, washed with PBS, and digitally photographed. (G) Size of individual tumors along the colon in WT treated with vehicle (n = 4) or oxaliplatin (n = 4) and IL25KO treated with vehicle (n = 7) or oxaliplatin (n = 7). (H) Total number and size of tumors. (I) Colon length in mice treated with the indicated treatment on 16 weeks. (J) Representative immunofluorescent stains for TUNEL in colonic sections from WT and IL25KO treated with vehicle or oxaliplatin (left). Statistical analysis of Tunel staining in WT and IL25KO tumors (right). Data present as mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.