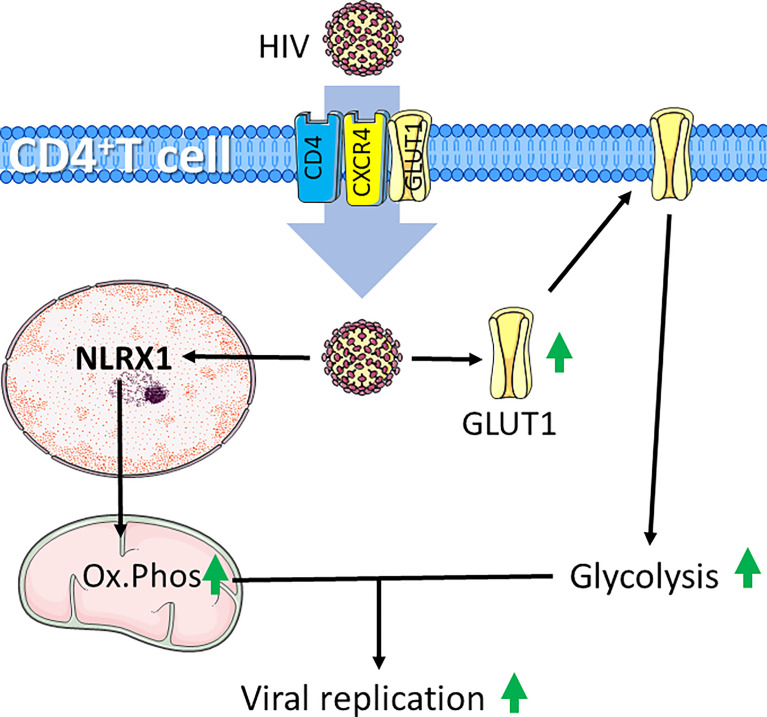
Figure 4.
HIV infection induces increased glycolysis and mitochondrial respiration in CD4+ T cells. HIV infects CD4+ T cells through interaction with CD4 and chemokine receptor CXCR4. HIV-infection supports glycolytic metabolism by increasing expression of the glucose transporter GLUT1, which can also be exploited to further infect CD4+ T cells. Additionally, HIV induces expression the of nucleotide-binding domain leucine-rich repeat-containing receptor X1 (NLRX1) to induce increased oxidative phosphorylation (Ox.Phos). The increased metabolic rate supports enhanced viral replication. Figure was created using assets from Servier Medical Art, licensed under a Creative Common Attribution 3.0 Generic License. http://smart.servier.com/.